 Water Bottle Rockets
Water Bottle Rockets


Click

Bottle rockets are excellent devices for investigating Newton's Three Laws of Motion.
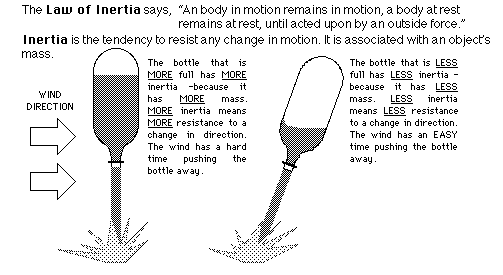
 The rocket will remain on the launch pad until an unbalanced force is exerted propelling the rocket upward (???? Law).
The rocket will remain on the launch pad until an unbalanced force is exerted propelling the rocket upward (???? Law).
 The amount of force depends upon how much air you pumped inside the rocket (???? Law). You can increase the force further by adding a small amount of water to the rocket. This increases the mass the rocket expels by the air pressure.
The amount of force depends upon how much air you pumped inside the rocket (???? Law). You can increase the force further by adding a small amount of water to the rocket. This increases the mass the rocket expels by the air pressure.
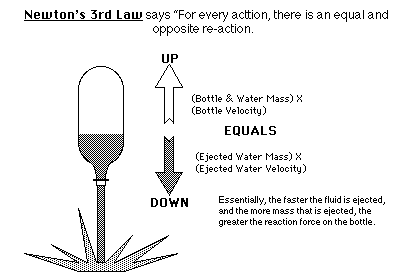
 Finally, the action force of the air (and water) as it rushes out the nozzle creates an equal and opposite reaction force propelling the rocket upward (???? Law).
Finally, the action force of the air (and water) as it rushes out the nozzle creates an equal and opposite reaction force propelling the rocket upward (???? Law).

Building a Bottle Rocket
Stability and Control Systems
Making a rocket stable requires some form of control system. There are three we are going to focus on.
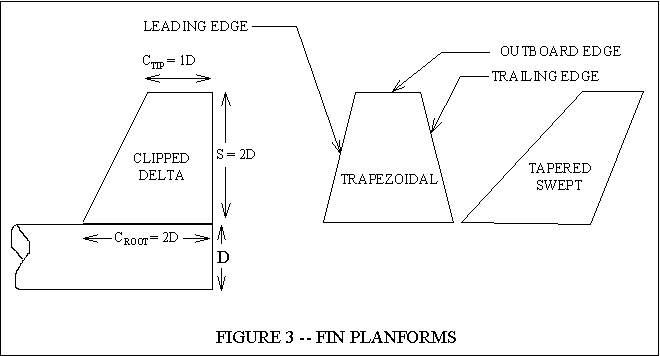
Fins-This helps keep the rocket staight up (stabilizing) The fins raise up from the rocket body for the purpose of giving the rocket directional stability. Usually located at the rear of the rocket.
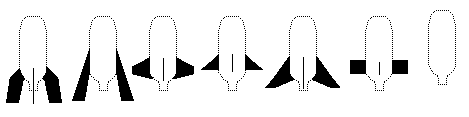
Nose cone--The front surface of a rocket, generally pointed in shape. It reduces drag (the resistance of moving air) by moving the air smoothly around the rocket.
Mass-- All matter, regardless of size, mass, or shape, has a point inside called the center of mass (CM).The center of mass is the exact spot where all of the mass of that object is perfectly balanced.
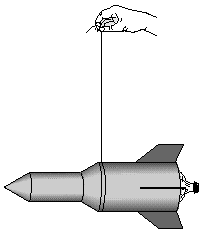
In addition to center of mass, there is another important center inside the rocket that affects its flight. This is the center of pressure (CP).

The center of pressure exists only when air is flowing past the moving rocket. This flowing air, rubbing and pushing against the outer surface of the rocket, can cause it to begin moving in a wild manner.

Tips on Building a Bottle Rocket
Perform to Center of Mass balance test. If you have time the Center of Pressure swing test.


