London Summer Seminar
2000/Ukraine
Black
Sea coasts zone of Ukraine.
"Black Sea Environmental
Priorities Study. Ukraine".
ISBN 92-1-126094-9.United National Publications Sales
No. E.98. III.B.16 Black Sea
Studies.
United Nations Publications, New
York, 1998.
Population and Economy. Demographic and Employment
Trends.
Since 1991, there has been a
down hard population trend in Ukraine.
The rate of natural
population growth is negative and since
1994.
Net migration has also turned negative.
Levels of unemployment are increasing.
Population of the
Black Sea and Azov Sea regions
|
Regions (administrative territorial units) |
Population (millions of persons) |
|||
|
1970 |
1979 |
1989 |
1995 |
|
|
Ukraine Donetsk Zaporizhia Mikolayiv Odessa Kherson ARC CR, total |
47.1 4.9 1.8 1.2 2.4 1.0 1.8 13.0 |
49.8 5.2 2.0 1.2 2.5 1.2 2.2 14.2 |
51.7 5.3 2.1 1.3 2.6 1.2 2.5 15.1 |
51.7 5.3 2.1 1.4 2.6 1.3 2.6 15.2 |
Source: Economy of Ukraine. 1994-1995
Mortality rates in Ukraine
increased from 12,1 per thousand to 14,7.
Birth rates fell from 12,7
per thousand to 10,0.
Population density in the Black Sea and Azov Sea regions
|
Regions |
Population density (person/km2) |
|
Donetsk Zaporizhia Mikolayiv Odessa Kherson ARC Ukraine |
198.8 77.0 55.0 78.3 44.7 85.4 85.7 |
Source:
Economy of Ukraine.
Thus, the general demographic situation in Ukraine including its coastal regions is not favourable and is worsening. Morbidity and mortality rates, especially infant's mortality is high. This situation has been brought on by factors such as the unfavourable demographic structure in herited from the former Soviet Union, the economic crisis, the unsatisfactory socio-economic conditions in many regions of Ukraine, and the low level of social development.
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Black
Sea coasts zone of Ukraine.
"Black Sea Environmental
Priorities Study. Ukraine".
ISBN 92-1-126094-9.United National Publications Sales
No. E.98. III.B.16 Black Sea
Studies.
United Nations Publications, New
York, 1998.
Economic Overview.
The Ukrainian economy
is facing a serious and growing crisis.
Macroeconomic indices for
1990-1995 illustrate the economic crisis in Ukraine, one without parallel among developed countries since
World War II except for the NIS.
GDP has fallen by 55%,
national income by 59%.
Consumption has been reduced
by 32%.
Major economic indices for
Ukraine, 1990-1995
|
Indices |
Years / % of previous year |
|||||
|
1990 |
1991 |
1992 |
1993 |
1994 |
1995 |
|
|
GDP* GDP** National Income** Industrial Output** |
-4.0 -2.4 -2.4 -0.1 |
-8.7 -13.5 -13.4 -4.8 |
-9.9 -16.8 -17.5 -6.4 |
-17.1 -14.2 -14.9 -7.6 |
-23.0 -23.0 -24.5 -27.7 |
-10.3 -11.8 -11.5 |
*
Official statistics and estimations of national economists.
** Estimations of the World
Bank
Source: Real Economy and Its Sectors. 1996.
Major trends in the industrial sector.
From 1991-1995, industrial output of the coastal regions declined dramatically.
Indices of industrial output
in coastal regions (1975=100)
|
Regions |
Total industrial output |
||||||
|
1985 |
1990 |
1991 |
1992 |
1993 |
1994 |
1995 |
|
|
Ukraine Donetsk Zaporizhia Mikolayiv Odessa Kherson ARC |
144 132 144 145 143 147 147 |
167 153 167 168 166 170 171 |
158 143 167 167 164 171 158 |
148 132 160 150 164 157 147 |
135 120 147 137 150 144 134 |
87 78 95 88 97 93 87 |
72 64 78 73 80 76 71 |
Source:
Economy of Ukraine, 1994-1995.
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Black
Sea coasts zone of Ukraine.
"Black Sea Environmental
Priorities Study. Ukraine".
ISBN 92-1-126094-9.United National Publications Sales
No. E.98. III.B.16 Black Sea
Studies.
United Nations Publications, New
York, 1998.
Pollution. Municipal Sewage.
Municipal Sources of Liquid
and Solid Waste of Selected Black Sea Regions
|
Liquid Waste |
Liquid Waste |
|||||||
|
Source |
Volume (m3/y) |
BOD5 Load (t/y) |
TSS Load (t/y) |
Total N Load (t/y) |
Total P Load (t/y) |
Oil Load (t/y) |
Putresible Load (t/y) |
Infection Load (t/y) |
|
Total Mikolayiv region Total Odessa region Total ARC TOTALS |
36,401 88,343 139,197 263,941 |
2,523 10,570 5,547 18,641 |
4,518 20,023 9,301 33,843 |
892 3,737 4,211 8,840 |
416 1,021 1,140 2,577 |
4,831 5,167 14,139 24,138 |
199,763 445,438 619,050 1,264,252 |
2,334 4,506 2,395 9,235 |
Source: Assessment of Land-based Sources of water and
Land Pollution in the Ukrainian Black Sea Coast. 1996.
Industrial Effluents. Aquatic Pollution
Concentration of 19 heavy
metals frequently exceeds the MACs in all Black Sea coast areas. The most
serious offenders are copper, zinc, cadmium, cobalt, nickel and chromium. The
load from the industrial sources is the following.
Industrial Sources of Liquid Waste for Selected Black Sea Regions
|
Liquid Waste |
||||||
|
Source |
Volume (m3/y) |
BOD5 Load (t/y) |
TSS Load (t/y) |
Total N Load (t/y) |
Total P Load (t/y) |
Oil Load (t/y) |
|
Total Mikolayiv region Total Odessa region Total ARC TOTALS |
1,343 101,833 15,157 118,333 |
669 29,858 6,003 36,531 |
2,637 13,048 54,743 70,428 |
29 26,113 4,813 30,954 |
1 15 1,683 1,699 |
210 62,700 8 62,918 |
Source: Assessment of Land-based Sources of water and
Land Pollution in the Ukrainian Black Sea Coast. 1996.
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Black
Sea coasts zone of Ukraine.
"Black Sea Environmental
Priorities Study. Ukraine".
ISBN 92-1-126094-9.United National Publications Sales
No. E.98. III.B.16 Black Sea
Studies.
United
Nations Publications, New York, 1998.
Atmospheric emissions.
· The dynamics of air pollutant emissions by industrial in the coastal
zones are similar to pollutant dynamics nationally.
· Air pollution there mainly comes from the metallurgical, energy,
coal mining and chemical industries.
· Due to the sharp decline in industrial output throughout Ukraine
and in these industries in particular, total emissions have decreased
dramatically.
Pollutant emission loads in
Black Sea and Azov Sea regions
|
Regions |
Pollutant emission loads |
||
|
1985 |
1990 |
1991 |
|
|
Donetsk Zaporizhia ARC Mikolayiv Odessa Kherson Total Ukraine |
142,8 39,2 37,5 15,6 15,8 12,2 31,2 |
116,6 32,6 25,5 12,2 12,8 9,3 25,8 |
108,5 27,2 22,3 11,1 11,8 9,6 23,7 |
Source:
National Report, 1992
Integrated Air Pollution Index for Selected cities in the Black Sea and Azov Sea Regions
|
Region |
City |
Major air polluting indastries |
Integrated Air Pollution Index (IAPI) |
||||
|
1991 |
1992 |
1993 |
1994 |
||||
|
Donetsk |
Donetsk Mariupol |
Coal, energy,
oil refinery, engeneering . Metallurgy,
electronics, energy |
163.2 133.7 |
186.2 108.0 |
87.7 NA
|
36.0 10.2 |
|
|
Zaporizhia |
Zaporizhia |
Metallurgy,
energy, engineering, transport
|
156,3
|
63.7 |
19.9 |
15.4 |
|
|
Mikolayiv |
Mikolayiv |
Shipbuilding,
electronics, energy |
52.3 |
35.0 |
7.6 |
8.8 |
|
|
Kherson |
Kherson |
Energy, machine-building, oil refinery,
construction |
52.3 |
35.0 |
7.6 |
8.8 |
|
|
Odessa |
Odessa Izmail |
Oil refinery,
machine-building, energy, constr. Marine
transport, food |
52.6 3.5 |
81.7 3.4 |
26.1 NA |
26.6 5.5 |
|
|
ARC |
Simferopol Yalta Kerch |
Chemicals,
energy, transp. Food, transport Metallurgy,
construction |
17.8 9.3 7.3 |
18.2 4.1 18.7 |
3.5 10.1 7.9 |
4.5 3.0 10.3 |
|
Source:
Yearbook 1986,88,93.95, the State Committee of Hydrometeorology
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Black
Sea coasts zone of Ukraine.
"Black Sea Environmental
Priorities Study. Ukraine".
ISBN 92-1-126094-9.United National Publications Sales
No. E.98. III.B.16 Black Sea
Studies.
United
Nations Publications, New York, 1998.
Institutional and Legislative Changes.
Following the adoption of
the new Constitution of Ukraine on 28 July
1996, considerable changes in the governmental institutional structure, including environmental bodies, are
being planned.
The following will be among
the key responsibilities of the Ministry for Environmental Protection and
Nuclear Safety:
·
Development of regional environmental monitoring systems and regional
environmental information systems;
·
Elaboration of compulsory rules, techniques, regulations directives and
guidelines on environmental protection;
·
Development, implementation and monitoring of specific environmental
programs;
·
Enhancement of environmental management capacity of State and local
levels;
·
Developing systems for environmental audits and environmental licensing;
·
Creation of environmental funds in the State budget
·
Organising competitive bidding on governmental contracts for
environmental investments;
·
Allocating permits for special use of natural resources, solid waste,
disposal and discharges and emissions of pollutants, and;
·
Creation of a system of environmental insurance.
Criteria for Setting Priorities.
Experience and analysis of the
specific problems of the Ukrainian Black Sea coastal zone, the following
criteria were chosen in rough order of priority:
1.
Losses from environmental damage to human health or health costa. Estimated by child mortality, child
pathology, morbidity, effect on life expectancy, ratio of mortality and birth
rates in comparison to ecologically pristine areas;
2.
Economic and ecological losses due to declining bio- productivity and
bio-diversity of terrestrial and marine ecosystems caused by environmental
pollution;
3.
"hot spots" and danger of irreversible damage to the natural
environmental;
4.
low-cost environmental protection measures and "win-win"
investments;
5.
ecological benefits/cost ratio
or net social benefits maximisation.
Those measures that result
in equivalent degrees of environmental protection utilising fewer funds and in
a shorter time period are preferable.
Also,
the renovation and construction of water treatment facilities at "hot
spots" are given high priority.
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Socio-Economical situation in the coastal region
of Ukraine and Odessa area.
Ukrainian National
Academy of Science. Institute of Market problem and Economic-Ecological
Research.
Short demographical report.
By the end of 1999 the
population of the coastal zone was as follows;
Kherson area - 12371000
Mykolayiv area - 13099000
Odessa area - 25286000
Odessa city - over 1 mln.
For the 11 months of 1999 in
Odessa area there were registered;
18300
-newborns.
32500 -
deaths (the natural decrease of population
- 14200
people.
The same period of 1999 - 13000).
The number of newborns for 100
dead - 56,2. (60 - for the same period of 1998).
The main causes of death in
1999 were;
·
Heart and vassal diseases (60%);
·
Oncology (14,7%);
·
Accidents, murders, suicides and other external
factors;
·
0,8% of
all total deaths were in children up to 12 months old.
In 1999 there were 16.2 thousand of marriages and
8,2 thousand of divorces. (In
1998 -15.2 and
8,1
accordingly).
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Socio-Economical situation in the coastal region
of Ukraine and Odessa area.
Ukrainian National
Academy of Science. Institute of Market problem and Economic-Ecological
Research.
The Employment Sphere
The Dynamics of Labor Costs
By the 1998 the share of highly-paid positions
had decreased 3 times,
of middle- paid positions - 4
times. At the same a share
of a low-paid positions had increased 7,5
times.
Simultaneously, we observe
the decrease of the real wages.
The dynamics of the work positions with high, middle
and low wages in %.
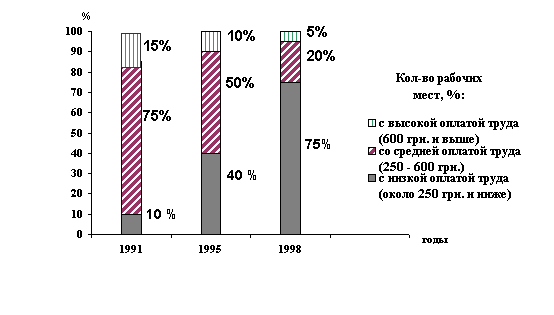
Work positions High (600 ukr. hrvn. and higher) Middle (250-600) Low (250 and more low) years
The disqualification of considerable population
groups, the loss of social markers and moral principles are obvious.
The number of unemployed - 1,7
mln. for coastal area (24 per 1
position).
This year there will be 600 thousand people laid out in the sphere of
industry.
All together there will be 3-7 mln.
people looking for a job in the region.
In the group of young people (15-24 years old). the unemployment is 3 times higher than in
the other age groups.
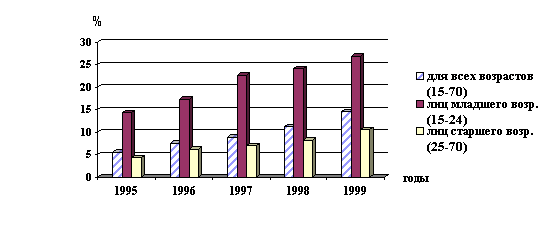 Dynamics of unemployment. Age structure.
Dynamics of unemployment. Age structure.
All
ages (15-70) Youth (15-24) Old (25-70) years
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Socio-Economical situation in the coastal region
of Ukraine and Odessa area.
Ukrainian National
Academy of Science. Institute of Market problem and Economic-Ecological
Research.
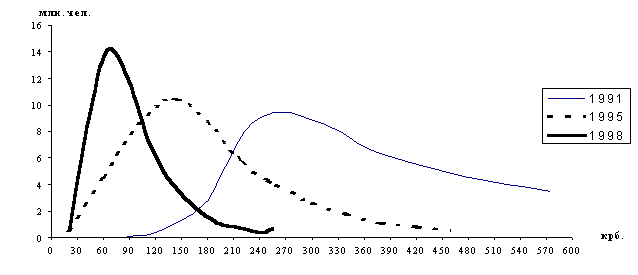
The Dynamics of Population Incomes.
According to the border of the lowest life support level (90,6 Ukr.
hrivnas, starting July, 2000 - 106 Ukr. hrivnas) -approximately 40% of the population is below this level.
mln.
of citizens
The total monthly average income of the population
|
mln.
of citizens |
|
krb. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1991 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
krb. |
87,5 |
112,5 |
137,5 |
162,5 |
182,5 |
225,0 |
275,0 |
325,0 |
375,0 |
475,0 |
575,0 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
mln.
of citizens |
0,05 |
0,25 |
0,85 |
1,75 |
2,75 |
8,2 |
9,4 |
8,25 |
6,4 |
4,6 |
3,5 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
1995 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
krb. |
20 |
60 |
100 |
140 |
180 |
220 |
260 |
300 |
340 |
380 |
420 |
460 |
500 |
|||||||||||||||
|
mln.
of citizens |
0,5 |
4,5 |
8,5 |
10,5 |
8,7 |
5,6 |
4,0 |
2,6 |
1,8 |
1,1 |
0,8 |
0,5 |
|
|||||||||||||||
|
1998 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
krb. |
21 |
38,5 |
63,5 |
89,0 |
114,5 |
140,0 |
165,5 |
190,5 |
216,0 |
241,5 |
254 |
|||||||||||||||||
|
mln.
of citizens |
0,55 |
7,3 |
14,1 |
11,9 |
6,95 |
3,95 |
2,25 |
1,15 |
0,75 |
0,4 |
0,7 |
|||||||||||||||||
The ratio between the incomes of the richest 10% of the population and the poorest 10% is as follows:
1991 - 4.5:1.
1995 - 6.4:1.
1998 - 37 :1.
The comparison of the 1991 and 1998 data
demonstrates the destruction and disappearance of the whole middle class - the
main and only possible basis for the social reforms in each and every society. Today in Ukraine there is only one
strategy for this group of population - survival at any coast.
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Socio-Economical situation in the coastal region
of Ukraine and Odessa area.
Ukrainian National
Academy of Science. Institute of Market problem and Economic-Ecological
Research.
The Evaluation of Nominal Wages in Odessa Region
In general in Ukraine the
share of wages in the structure of money income has decreased from 68% in 1990 to 48% in 1999.
Dynamics of incomes and payments of the Odessa area population
Dec.
96 Jul. 97 Dec. 97 Nov. 98 Nov. 99
Apr. 2000 Hrv./month
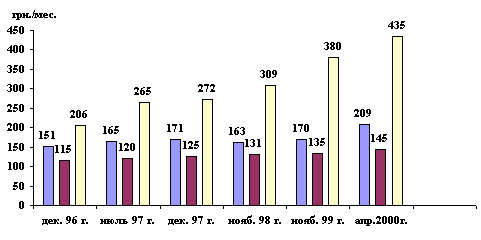
Deficit
per capita in % Dec. 96 Jul. 97
Dec. 97 Nov. 98 Nov. 99 Apr. 2000 Average
wage of all categories of employees Average
wage for State Budget organizations Minimal living budget per capita (one month) The difference between
the nominal wages and need necessary expenses (% to the wages)
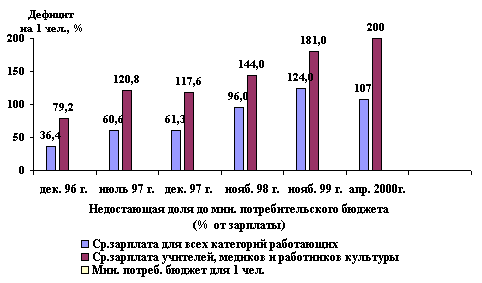
London
Summer Seminar 2000/Ukraine
Socio-Economical situation in the coastal region
of Ukraine and Odessa area.
Ukrainian National
Academy of Science. Institute of Market problem and Economic-Ecological
Research.
Short conclusions
·
The
system of social support in the country is far from ideal;
·
The
level of social support depends on the general poor economic growth;
·
In
the region there are no long-term programs of social protection of the
population.
·
Besides
the deficit of financial means the main financial capital is concentrated in a
bank system, new structures and underground financial turnover the
representatives of which are not interested in social investments;
·
In a
vast number of the social sphere sections the alternative opportunities are
absent, the competition relations are not functioning.
·
There
is a keen necessity of an active influence on the structure of the labor
market.
·
An
extreme attention to the work with young people is needed, attention to the
sphere, where the increase of low qualified labor force is progressing.
·
Only
a complex approach can positively influence the economic state and in general
social development of Ukraine.