
September 7
1776 American Revolution: World's first submarine attack:
On this day in 1776, during the Revolutionary War, the American submersible craft Turtle attempts to attach a time bomb to the hull of British Admiral Richard Howe's flagship Eagle in New York Harbor. It was the first use of a submarine in warfare.
Submarines were first built by Dutch inventor Cornelius van Drebel in the early 17th century, but it was not until 150 years later that they were first used in naval combat. David Bushnell, an American inventor, began building underwater mines while a student at Yale University. Deciding that a submarine would be the best means of delivering his mines in warfare, he built an eight-foot-long wooden submersible that was christened the Turtle for its shape. Large enough to accommodate one operator, the submarine was entirely hand-powered. Lead ballast kept the craft balanced.
Donated to the Patriot cause after the outbreak of war with Britain in 1775, Ezra Lee piloted the craft unnoticed out to the 64-gun HMS Eagle in New York Harbor on September 7, 1776. As Lee worked to anchor a time bomb to the hull, he could see British seamen on the deck above, but they failed to notice the strange craft below the surface. Lee had almost secured the bomb when his boring tools failed to penetrate a layer of iron sheathing. He retreated, and the bomb exploded nearby, causing no harm to either the Eagle or the Turtle.
During the next week, the Turtle made several more attempts to sink British ships on the Hudson River, but each time it failed, owing to the operator's lack of skill. Only Bushnell was really able to competently execute the submarine's complicated functions, but because of his physical frailty he was unable to pilot the Turtle in any of its combat missions. During the Battle of Fort Lee, the Turtle was lost when the American sloop transporting it was sunk by the British.
Despite the failures of the Turtle, General George Washington gave Bushnell a commission as an Army engineer, and the drifting mines he constructed destroyed the British frigate Cereberus and wreaked havoc against other British ships. After the war, he became commander of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers stationed at West Point. (History.com)

1797 The USS Constellation, the second of the nation's new warships, is launched. [For further details, Click here.]

1813 United States nicknamed Uncle Sam:
On this day in 1813, the United States gets its nickname, Uncle Sam. The name is linked to Samuel Wilson, a meat packer from Troy, New York, who supplied barrels of beef to the United States Army during the War of 1812. Wilson (1766-1854) stamped the barrels with "U.S." for United States, but soldiers began referring to the grub as "Uncle Sam's." The local newspaper picked up on the story and Uncle Sam eventually gained widespread acceptance as the nickname for the U.S. federal government.
In the late 1860s and 1870s, political cartoonist Thomas Nast (1840-1902) began popularizing the image of Uncle Sam. Nast continued to evolve the image, eventually giving Sam the white beard and stars-and-stripes suit that are associated with the character today. The German-born Nast was also credited with creating the modern image of Santa Claus as well as coming up with the donkey as a symbol for the Democratic Party and the elephant as a symbol for the Republicans. Nast also famously lampooned the corruption of New York City's Tammany Hall in his editorial cartoons and was, in part, responsible for the downfall of Tammany leader William Tweed.

Perhaps the most famous image of Uncle Sam was created by artist James Montgomery Flagg (1877-1960). In Flagg's version, Uncle Sam wears a tall top hat and blue jacket and is pointing straight ahead at the viewer. During World War I, this portrait of Sam with the words "I Want You For The U.S. Army" was used as a recruiting poster. The image, which became immensely popular, was first used on the cover of Leslie's Weekly in July 1916 with the title "What Are You Doing for Preparedness?" The poster was widely distributed and has subsequently been re-used numerous times with different captions.
In September 1961, the U.S. Congress recognized Samuel Wilson as "the progenitor of America's national symbol of Uncle Sam." Wilson died at age 88 in 1854, and was buried next to his wife Betsey Mann in the Oakwood Cemetery in Troy, New York, the town that calls itself "The Home of Uncle Sam." (History.com)


1814 35-year-old amateur poet, Francis Scott Key, writes the poem "Defense of Fort McHenry" after witnessing the bombardment of Fort McHenry in Baltimore, Maryland, by the rockets and artillery of Royal Navy ships off Chesapeake Bay. The poem will later be set to music and renamed "The Star-Spangled Banner." (Glover)
1891 Birth: Brian Horrocks: British military officer: He is chiefly remembered as the commander of XXX Corps in Operation Market Garden and other operations during World War II.
Horrocks: We, as a maritime power with territories all over the world, have had considerable experience in landing troops from the sea; the Germans have not. Nevertheless, given time there was little doubt that they could eventually stage a large-scale invasion of Britain, so our defence had to be organized with the utmost care to make up for our lack of numbers. It proved a very difficult problem.
1901 The Boxer Protocol:
[The protocol was] signed on September 7, between the Qing Empire of China and the Eight-Nation Alliance—Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States—plus Belgium, Spain and the Netherlands after China's defeat in the intervention to put down the Boxer Uprising
1903 (September 7-12): A US naval force protects American interests in rebellion-torn Syria.
1914 World War I: Various:
Battle of the Marne: Kluck turns his entire army westward in savage counterattacks, halting the French and forcing them to fall back.
For the next three days the German forces were unable to break through the Allied lines. At one stage the French 6th Army came close to defeat and were only saved by the use of Paris taxis to rush 6,000 reserve troops to the front line.
Sir John French's First Despatch as British Commander-in-Chief:

My Lord: I have the honour to report the proceedings of the field force under my command up to the time of rendering this dispatch. 1. The transport of the troops from England both by sea and by rail was effected in the best order and without a check. Each unit arrived at its destination in this country well within the scheduled time. The concentration was practically complete on the evening of Friday, the 21st ultimo, and I was able to make dispositions to move the force during Saturday, the 22nd, to positions I considered most favourable from which to commence operations which the French Commander in Chief, Gen. Joffre, requested me to undertake in pursuance of his plans in prosecution of the campaign.
Telegram to President Woodrow Wilson from Kaiser Wilhelm II:

I feel it my duty, Mr. President, to inform you as the most prominent representative of principles of humanity, that after taking the French fortress of Longwy, my troops discovered there thousands of dumdum cartridges made by special government machinery. The same kind of ammunition was found on killed and wounded troops and prisoners, also on the British troops. You know what terrible wounds and suffering these bullets inflict and that their use is strictly forbidden by the established rules of international law.
I therefore address a solemn protest to you against this kind of warfare, which, owing to the methods of our adversaries, has become one of the most barbarous known in history. Not only have they employed these atrocious weapons, but the Belgian Government has openly encouraged and, since long, carefully prepared the participation of the Belgian civil population in the fighting. The atrocities committed even by women and priests in this guerrilla warfare, also on wounded soldiers, medical staff and nurses, doctors killed, hospitals attacked by rifle fire, were such that my generals finally were compelled to take the most drastic measures in order to punish the guilty and to frighten the bloodthirsty population from continuing their work of vile murder and horror. Some villages and even the old town of Loewen [Louvain], excepting the fine hotel de ville, had to be destroyed in self-defence and for the protection of my troops. My heart bleeds when I see that such measures have become unavoidable and when I think of the numerous innocent people who lose their home and property as a consequence of the barbarous behaviour of those criminals.
Official Report by the Belgian Ambassador to Turkey, Baron Guillaume:
A week ago a rupture appeared probable. The Government not only did not send back the German crews of the Goeben and the Breslau, but hundreds of sailors and artillerymen were seen arriving from Germany, to serve both in the naval forces and in the batteries guarding the Straits. The moment therefore appeared near, when the sense of national dignity would oblige the three Allied Powers to put a limit to the provocations of Turkey. Their Ambassadors then began to prepare for departure and I had the honour of informing you of this by telegraph, adding that in the event of my receiving my passports myself, I proposed to entrust the protection of the Belgians residing in Turkey to the Ambassador of the United States.

1914 List Regiment: (Sep 1-Oct 7): Hitler's regiment continues a short but intensive basic training program, which is held in the premises of a large public school on the Elizabeth Platz in Munich. Hitler receives the first uniform of his life; basic greenish-grey with an "RIR 16" sown in red unto the epaulettes and a red stripe down the side of the trousers. The trousers are tucked into new leather boots, topped by a thick leather belt around the waist of the uniform jacket. [For further details, Click here.]
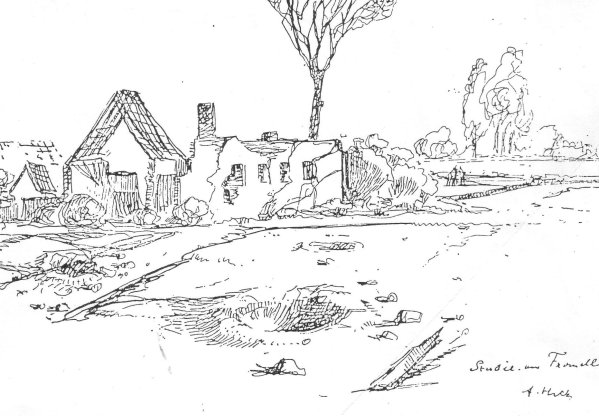

1915 World War I: List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler's 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment continues to occupy a position, at Fromelles—pictured above in a drawing by Hitler—on a level field with water channels, willow trees and willow stalks; in the distance towards the enemy lines lie an insignificant wood with barbed wire entanglements. Under the direction of their defense-minded commander, Lieutenant General Gustav Scanzoni von Lichtenfels, the regiment works ceaselessly day and night to further fortify their position at Fromelles while fighting off repeated assaults by the enemy. [For further details, Click here.]

Hitler and his fellow dispatch runners
1916 World War I: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler endures trench warfare in Flanders (Artois) with 3 Company, 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment [List Regiment]. [For further details, Click here.]

1917 World War I (July 22-September 8): Dispatch Runner Gefreiter Adolf Hitler serves at the front with 3 Company, 16 Bavarian Reserve Infantry Regiment during Phase 2 operations in Flanders. Most of their time in the trenches gas masks are worn, while English bombers attack from the air, and tanks attempt to advance over a long front through seas of mud. [For further details, Click here.]

1918 World War I (August 21-September 27): Gefreiter Adolf Hitler attends a signals training course in Nuremberg. [For further details, Click here.]

1931 Give Until It Hurts: George V announces he will be taking a STG 50,000 a year pay cut while the economic crisis continues.
1936 Birth: Buddy Holly:
If you took out a map of the United States and traced a line beginning at New Orleans and running up the Mississippi River to Memphis, the tip of your finger would pass through the very birthplace of rock and roll: a region where nearly every step in its early development took place and where nearly every significant contributor to that development was born. But if the foundation of rock and roll was mostly laid down within 100 miles of the Mississippi River in the mid-1950s, the blueprint for what would follow required the further contributions of a young man born 700 miles to the west on this day in 1936: Charles Harden Holley. Writing and performing under the name Buddy Holly, this Lubbock, Texas, native would have an influence on rock and roll that would far outlast his tragically shortened career. [For further details, Click here]
1938 Various:
France announces a partial mobilization in response to Hitler's demands on Czechoslovakia:
A crisis in Czechoslovakia threw Europe into turmoil in 1938. Czechoslovakia had been created in 1919. The new nation was created out of the old Austro-Hungarian Empire and it contained numerous nationalities : 3,200,000 Germans 7,450,000 Czechs 2,300,000 Slovaks 720,000 Magyars 560,000 Ruthenes 100,000 Poles. It was almost inevitable that trouble would occur between the various nationalities. This was especially true of the Germans who resented living under the rule of foreigners. The Germans mostly lived in the region on the western border with Germany—the Sudetenland.
Holocaust: Various:
Italy: All Jews naturalized after January 1, 1919, lose their citizenship.
Above all, for the majority of the Italians, the Jews are considered in spite of everything else . . . like people that coincide for all the aspects to their race, and the persecution decreed against them leaves everyone embittered and irritated because of things that are considered way out of our Roman sensibility.

Church and Reich: Pope Pius XI during a reception for Catholic pilgrims from Belgium, from condemning the participation of Catholics in anti-Semitic movements and to have added that Christians, the spiritual descendants of the Patriarch Abraham, were "spiritually Semites." This statement is omitted by all the Italian papers, including L'Osservatore Romano. Mussolini, in his November 1919 speech to the Congress of the Party in Rome, and again in 1921, clearly stressed that: "I mean to say that Fascism has to deal with the race problem. The Fascists have to take care of the health of the race that will make history.
1939 World War II: Various
Poland: Mobile spearheads reach the Narev river. Cracow surrenders, while German forces under von Reichenau advance closer to Warsaw. Jewish property was seized and several synagogues were burned down. By March 1941, approximately 40,000 Jews had been expelled to neighboring towns, their property confiscated. At the same time, a sealed-off ghetto was established. The worst problems were the result of overcrowding and poor sanitary conditions. The population was impoverished, and the Germans set up several factories to exploit the cheap labor in the ghetto.

Heydrich tells his division heads that the Polish leadership must be 'neutralized.' The Einsatzgruppen already has lists of people considered to be hostile to Germany, which includes members of Polish patriotic organizations, communists, clergymen, noblemen, and Jews. (THP)
Western front: Sep 7-9: In an attempt to relieve Poland, as per treaty obligations, without actually opening up another front, French forces cross the German border at three different locations: near Saarbrucken, Saarlouis, and Zweibrucken. The French meet little resistance due to the fact that Hitler, who has no desire to open another front himself, has ordered German units near the border not to engage the French units unless they are attacked and forced to return fire. The transfer of troops to Poland has left only eleven regular divisions plus the equivalent of one division of fortress troops defending the western frontier. These are supported by 35 recently formed divisions of second, third, and fourth-line troops. There are no armored or motorized units facing west; they have all been transferred to the East. (THP)
London: The BBC commences daily radio broadcasts in Polish.
Holocaust: Poland:

Anti-Semitism had long been evident in Poland. Jews were not considered Poles and, as in Nazi Germany, were defined as a race. It appears that, until 1939, Poland saw its destiny as tied to Germany's and its policies toward Jews mirrored those of Germany—forced emigration. This was all to change with the Nazi invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939. The consequences of this invasion were disastrous for Poland as a nation and, especially for Poland's Jewish population. Immediately following the invasion, Heinrich Himmler was appointed to take measures to strengthen German ethnicity in the occupied territories and to create lebensraum, or living space for German citizens. To this end, Himmler created special task forces within the SS, the Einsatzgruppen, and placed them under the command of Reinhard Heydrich.

1940 World War II: Various:
The Blitz begins:

On this day in 1940, 300 German bombers raid London, in the first of 57 consecutive nights of bombing. This bombing "blitzkrieg" (lightning war) would continue until May 1941.
After the successful occupation of France, it was only a matter of time before the Germans turned their sights across the Channel to England. Hitler wanted a submissive, neutralized Britain so that he could concentrate on his plans for the East, namely the land invasion of the Soviet Union, without interference. Since June, English vessels in the Channel had been attacked and aerial battles had been fought over Britain, as Germany attempted to wear down the Royal Air Force in anticipation of a land invasion. But with Germany failing to cripple Britain's air power, especially in the Battle of Britain, Hitler changed strategies. A land invasion was now ruled out as unrealistic; instead Hitler chose sheer terror as his weapon of choice.
British intelligence had had an inkling of the coming bombardment. Evidence of the large-scale movement of German barges in the Channel and the interrogation of German spies had led them to the correct conclusion; unfortunately, it was just as the London docks were suffering the onslaught of Day One of the Blitz. By the end of the day, German planes had dropped 337 tons of bombs on London. Even though civilian populations were not the primary target that day, the poorest of London slum areas—the East End—felt the fallout literally, from direct hits of errant bombs as well as the fires that broke out and spread throughout the vicinity. Four hundred and forty-eight civilians were killed that afternoon and evening.
A little past 8 p.m., British military units were alerted with the code name "Cromwell," meaning the German invasion had begun. A state of emergency broke out in England; even home defense units were put to the ready. One of Hitler's key strategic blunders of the war was to consistently underestimate the will and courage of the British people. They would not run or be cowed into submission. They would fight. (History.com)
[See: Why Did Hitler Lose The Battle of Britain?]US State Department Circular:
The Secretary of State on September, 6 sent the following instruction to diplomatic missions of the United States in all the other American republics. It is desired that you formally notify the Government to which you are accredited that the United States has acquired the right to lease naval and air bases in Newfoundland, and in the islands of Bermuda, the Bahamas, Jamaica, St. Lucia, Trinidad, and Antigua, and in British Guiana.
The Government of the United States has taken this step to strengthen its ability not only to defend the United States but in order the more effectively to cooperate with the other American republics in the common defense of the hemisphere. The resulting facilities at these bases will, of course, be made available alike to all American republics on the fullest cooperative basis for the common defense of the hemisphere and in entire harmony with the spirit of the pronouncements made and the understandings reached at the conferences of Lima, Panama, and Habana.
Treaty of Craiova: Romania loses Southern Dobrudja to Bulgaria; imposed on Romania by Nazi Germany. Under its terms Romania cedes the southern part of Dobruja and agrees to participate in the organization of a population exchange. The 80,000 Romanians and Aromanians, most of them settled there since the end of the Second Balkan War in 1913 (see Treaty of Bucharest, 1913), when the territory was occupied by Romania, were forced to abandon their houses in southern Dobruja and resettled in the northern part, while 65,000 Bulgarians of the northern part had to leave for the Cadrilater.
1941 World War II: Various:
Finland: The offensive by German forces in northern Finland to capture the vital Lend-Lease port of Murmansk comes to a halt.
Murmansk faced its severest trials during the Second World War between 1941 and 1945. According to war veterans, it was an absolute hell where, by all military or civilian notions, nothing could have survived: steel and stones melted, but the people stood fast.
Ukraine: Mobile units under von Paulus achieve a breakthrough at Konotop.
1942 World War II: Various:
US President Roosevelt addresses the nation:

The responsibilities of the President in war time to protect the Nation are very grave. This total war, with our fighting fronts all over the world, makes the use of executive power far more essential than in any previous war. If we were invaded, the people of this country would expect the President to use any and all means to repel the invader. The Revolution and the War between the States was fought on our own soil but today this war will be won or lost on other continents and remote seas. I cannot tell what powers may have to be exercised in order to win this war. The American people can be sure that I will use my powers with a full sense of responsibility to the Constitution and to my country. The American people can also be sure that I shall not hesitate to use every power vested in me to accomplish the defeat of our enemies.
War in the Pacific: The first air evacuation of casualties to hospital ships off shore occurs at Guadalcanal.
[See: Guadlcanal Diary.]1943 World War II: Barbarossa: 17th Armee begins the evacuation of the Kuban bridgehead across the Strait of Kerch to the Crimea.
1944 World War II:
Rumania: now allied with the Soviet Union, declares war on Hungary, whose forces are still fighting on the German side.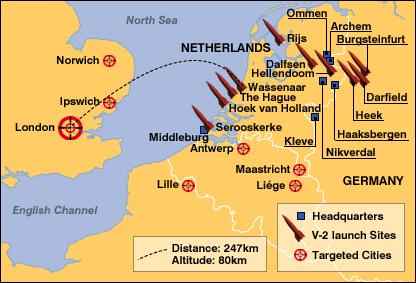
London: The day before the first V-2 rocket is fired at London, British Home Secretary, Herbert Morrison, issues an upbeat statement announcing that "the Battle of London has been won."
[See: Wunderwaffen: Hitler's Deception and the History of Rocketry.]
1946 Nuremberg Tribunal: The justices meet to discuss verdicts in the Major War Criminals Trial. (See: 30 September 1946)
1950 Cold War: United Nations defeats Soviet motion:
Slightly more than two months after the United Nations approved a U.S. resolution calling for the use of force to repel the communist North Korean invasion of South Korea, the Security Council rejects a Soviet resolution that would condemn the American bombing of North Korea. The Security Council action was another victory for the United States in securing U.N. support for the war in Korea. [For further details, Click here]
1956 Spandau Prison: From Spandau: The Secret Diaries, by Albert Speer:
Before going into the yard this afternoon we had to wait for Hess. When he arrived at last, Doenitz said to him, "If I had a mark, Herr Hess, for every quarter-hour I've had to wait for you in the past eleven years, I'd be a rich man." Hess retorted without hesitation, "And if I, Herr Doenitz, had only a single pfennig for every useless word you've addressed to me in these eleven years, I'd be much richer than you." Recently Doenitz has been showing his irritation with the preferential treatment of Hess by speaking of him as "Herr Baron." Lately he has formed the habit of posting himself ten paces in front of Hess and staring at him for minutes at a time. Sometimes I then post myself beside Hess and stare back, which makes him stop his rudeness.
1991 The Baltic states are recognized by Russia.
Edited by Levi Bookin (Copy editor)
levi.bookin@gmail.com



Click to join 3rdReichStudies



Disclaimer: This site includes diverse and controversial materials—such as excerpts from the writings of racists and anti-Semites—so that its readers can learn the nature and extent of hate and anti-Semitic discourse. It is our sincere belief that only the informed citizen can prevail over the ignorance of Racialist "thought." Far from approving these writings, this site condemns racism in all of its forms and manifestations.
Fair Use Notice: This site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of historical, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, environmental, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a "fair use" of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond 'fair use', you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.
Please Note: The list-owner and moderators of 3rdReichStudies are not responsible for, and do not necessarily approve of, the random ads placed on our pages by our web server. They are, unfortunately, the price one pays for a 'free' website.