
September 12
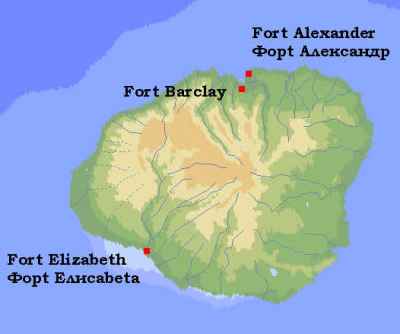
1816 Hawaii: Russian nationals begin construction of Fort Elizabeth on the Hawaiian island of Kauai, commanding Waimea Bay. Hawaiian King Kamehameha acts before the construction is done, driving the Russians off the island by force. The Hawaiians will name the stronghold Fort Hipo. (Russ)
[See: Countdown to Infamy: Pearl Harbor.]1839 Japan: Takasugi Shinsaku (Tani Umenosuke), a samurai from the Chōshū domain of Japan, is born. He will be an influential factor as one of the most extreme advocates of a policy of seclusion (Sakoku), and will contribute significantly to the Meiji Restoration. (Huber, Craig)
1855 September 12-November 4: A US military force invades the Fiji Islands in reprisal for alleged mistreatment of US nationals. Subsequent US military intervention in the Fiji Islands: 1858.
1885 Birth: Heinrich Hoffmann: Hitler's personal photographer and business partner, for years the only photographer in Germany authorized to snap Der Fuehrer's profile. Hoffmann's daughter will marry Hitler Youth leader Baldur von Schirach, while his secretary, Eva Braun, will eventually marry Hitler himself. After the collapse, Hoffmann will earn Goering's scorn by working for the IMT cataloguing his photographs for the prosecution. "He made a million Marks on my photos, now he's working to hang me with them!" Hoffman will be sentenced to five years in a labor camp in 1947 as a war profiteer, but will be released shortly afterwards and live comfortably on income from his photo files, which will contain more than 2.5 million photographs. Note: The majority of the images of Hitler in existence are Hoffman's work, and it is rare to pick up any book on World War II, Hitler, etc., without finding a few.
1897 Volkishness: Adolf Josef Lanz: now Brother Georg, takes his vows as a Cistercian monk at Heiligenkreuz Abbey. Lanz's novice-master is Nivard Schloegl, a bible scholar and expert on oriental languages. Schloegl disdains the Jews as an arrogant and exclusive religious group. His bible translations are placed on the Index of Forbidden Books by the Catholic Church because of his anti-Semitic prejudice. (THP) 1913 Birth: Jesse Owens:

In Berlin, Mr. Owens, who was black, scored a triumph that would come to be regarded as not only athletic but also political. Adolf Hitler had intended the Berlin Games to be a showcase for the Nazi doctrine of Aryan supremacy. . . .
The United States Olympic track team, of 66 athletes, included 10 blacks. The Nazis derided the Americans for relying on what the Nazis called an inferior race, but of the 11 individual gold medals in track won by the American men, six were won by blacks.
The hero was Mr. Owens. He won the 100-meter dash in 10.3 seconds, the 200-meter dash in 20.7 seconds and the broad jump at 26 feet 5 1/2 inches, and he led off for the United States team that won the 400-meter relay in 39.8 seconds.
His individual performances broke two Olympic records and, except for an excessive following wind, would have broken the third. The relay team broke the world record. His 100-meter and 200-meter times would have won Olympic medals through 1964, his broad- jump performance through 1968.
Actually, Mr. Owens had not been scheduled to run in the relay. Marty Glickman and Sam Stoller were, but American Olympic officials, led by Avery Brundage, wanted to avoid offending the Nazis. They replaced Mr. Glickman and Mr. Stoller, both Jews, with Mr. Owens and Ralph Metcalfe, both blacks.
Hitler did not congratulate any of the American black winners, a subject to which Mr,. Owens addressed himself for the rest of his life. "It was all right with me," he said years later, "I didn't go to Berlin to shake hands with him, anyway. All I know is that I'm here now, and Hitler isn't.
"When I came back, after all those stories about Hitler and his snub, I came back to my native country, and I couldn't ride in the front of the bus. I had to go to the back door. I couldn't live where I wanted. Now what's the difference?"
Having returned from Berlin, he received no telephone call from President Franklin D. Roosevelt, was not asked to visit the White House. Official recognition from his own country did not come until 1976, when President Gerald R. Ford presented him the Presidential Medal of Freedom. Three years later, President Carter gave him the Living Legends Award. [For further information, click here.]
1914 List Regiment (Sep 1-Oct 7):

Infantry Recuit Adolf Hitler's regiment continues a short but intensive basic training program, which is held in the premises of a large public school on the Elizabeth Platz in Munich. Hitler wears the first uniform of his life; basic greenish-grey with an "RIR 16" sown in red unto the epaulettes and a red stripe down the side of the trousers. The trousers are tucked into new leather boots, topped by a thick leather belt around the waist of the uniform jacket. [For further details, Click here.]
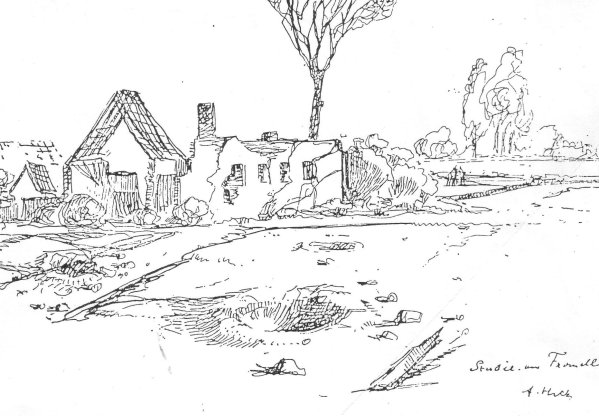

1915 World War I: List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler's 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment continues to occupy a position, at Fromelles—pictured above in a drawing by Hitler—on a level field with water channels, willow trees and willow stalks; in the distance towards the enemy lines lies an insignificant wood with barbed wire entanglements. Under the direction of their defense-minded commander, Lieutenant General Gustav Scanzoni von Lichtenfels, the regiment works ceaselessly day and night to further fortify their position at Fromelles while fighting off repeated assaults by the enemy. [For further details, Click here.]

Hitler and his fellow dispatch runners
1916 World War I: List Regiment: Gefreiter Adolf Hitler endures trench warfare in Flanders (Artois) with 3 Company, 16 Reserve Infantry Regiment. [For further details, Click here.]
1917 World War I: Various:
US Ambassador to Belgium, Brand Whitlock, to the US Secretary of State:
Towns were sacked and burned, homes were pillaged; in many places portions of the population, men, women, and children, were massed in public squares and mowed [sic] down by mitrailleuses [sic], and there were countless individual instances of an amazing and shameless brutality. The stories of these deeds gradually filtered into Brussels in ever increasing numbers as the days went by, brought by the refugees, who, in crowds, fled the stricken region in terror. It was difficult at first to believe them; but the stories persisted, and were told with such detail and on such authority that one could no longer doubt their essential truth. They became a matter of common knowledge and public notoriety; and they saturated the general mind with their horror.
List Regiment: Having been taken off the front by train for a two month rest, the regiment is guarding a camp near Mulhouse in Alsace, the only section of the front on German soil. During this slow time, not only will Hitler and his comrades get a well-deserved respite from the rigors of trench warfare, but the heavily censored news from the Front seems to be improving as well. The news of the collapse of the Russian Front and the further defeats of Italian arms is, however, tempered by the news that German munitions workers have gone on strike. This mix of events give an impression that the war on the Front is going well, but being undermined by defeatism on the home front.
[For further details, Click here.]1918 World War I: Various:
U.S. launches Saint-Mihiel offensive: The American Expeditionary Force (AEF) under the command of General John J. Pershing launches its first major offensive operation as an independent army during World War I . . . .
The attack began on September 12, 1918, with the advance of Allied tanks across the trenches at Saint-Mihiel, followed closely by the AEF's infantry troops. Foul weather plagued the offensive as much as the enemy troops, as the trenches filled with water and the fields turned to mud, bogging down many of the tanks. Despite the conditions, the attack proved successful—in part because the German command made the decision to abandon the salient—and greatly lifted the morale and confidence of Pershing's young army. By September 16, 1918, Saint-Mihiel and the surrounding area were free of German occupation. The American forces immediately shifted further south, to a new offensive near the Argonne Forest and the Meuse River, where they combined with British and French forces to further hammer the Germans, as the Allies moved ever closer to victory in World War I.
General Max von Gallwitz on the Battle of St Mihiel:
Before the attack on the St. Mihiel triangle the American troops had been greatly strengthened. Their divisions had been welded together into army corps. By the beginning of September we learned of the formation of an independent Pershing American army, which was lying between the second and eighth French armies. American divisions had fought honourably in the big battles which ended with the failure of our offensive at the Marne in July and August. It was an obvious suggestion to follow up this gradual development with some big feat, accomplished exclusively or largely by American troops under their own supreme command. An opportunity offered itself.

List Regiment: (August 21-September 27) Gefreiter Adolf Hitler attends a signals training course in Nuremberg. [For further details, Click here.]
1919 Weimar: Adolf Hitler attends his first meeting of the German Workers' Party (DAP). Hitler has been ordered by Captain Karl Mayr, his immediate superior, to attend as a spy for the army. (THP) Note: Hitler is less than impressed by the few dozen fellows sitting around the back room of a beer hall talking politics. As he is about to leave because of boredom, a gentleman begins to speak on a subject to which Hitler is violently opposed. Hitler seizes the floor and obliterates the gentleman's arguments to the extent that the humbled speaker leaves the hall. Anton Drexler, the founder of the little party, is impressed enough with Hitler's performance that he remarks to a colleague, 'He can speak! We can use him.' Drexler catches Hitler before he departs and places a pamphlet in his hands, asking him to read it and imploring him to attend the next meeting. Hitler is noncommittal.
1923 Weimar: Hitler speaks in Munich:

In fact the Revolution made three changes in our State: it internationalized the German State, the economic life of Germany, and the German people itself. Thereby Germany has been turned into a colony of the outside world. Those who were fed with the ideal of the International were in fact placed under the 'Diktat' of the International. They have their international State: today international finance is king.
1931 Holocaust: Berlin: On the evening of the Jewish New Year, Nazi gangs attack Jews returning from synagogue. (THP)

1932 Weimar: The Catholic Center Party deputies in the Reichstag vote for a Communist sponsored no-confidence motion against Papen's government. President Hindenburg again dissolves the Reichstag. (THP)
1933 Various:
Church and Reich: Euthanasia: Cardinal Bertram submits a letter of protest concerning the 'Law for the Prevention of Genetically Diseased Offspring' to Minister of the Interior Frick. (THP)
Though Hitler felt a particular urgency and hatred when dealing with Jews and Communists, he viewed the Catholic Church as a pernicious opponent, a deeply-entrenched threat that must be controlled and eventually uprooted from German life in order to establish his promised 'Thousand Year Reich'.
Nuclear science: Hungarian-American physicist Leo Szilard conceives of the idea of the nuclear chain reaction while waiting for a traffic light in Bloomsbury, London. [For further information, click here.]
1934 The Baltic States of Latvia, Estonia, and Lithuania sign a mutual non-aggression and cooperation treaty.
1936 Hitler makes a speech to the Labor Front in Nuremberg:

Some people say, 'He has brought out another plan.' When he had completed the first, why couldn't he leave us in peace? Now he is tackling problems that cannot be solved.' I say that they can be solved; there is no problem that cannot be, but faith is necessary. Think of the faith I had to have eighteen years ago, a single man on a lonely path. Yet I have come to leadership of the German people.
1937 Holocaust: The Romanian National Soldiers Front calls on Romanian citizens to deal with the "Jewish Plot."
1938 Various:
Sudetenland: In a speech in Nuremberg, Adolf Hitler demands self-determination for the Sudeten Germans in Czechoslovakia. (AP)
Holocaust: Italy orders the expulsion of all foreign Jews: (THP)
"Everywhere Italian partisans were active, Jewish partisans were among them. As many as 2,000 Jewish partisans fought in Italian partisan groups out of a total of 35,000 Jews in German-occupied Italy. Many Jews held high-ranking positions in the Resistance.”
1939 World War II: Various:

Poland: Admiral Wilhelm Canaris head of the Abwehr, protests to General Keitel that extensive shootings are planned in Poland, and that the nobility and intelligentsia are to be exterminated. The world, Canaris prophetically declares, will hold the German armed forces responsible. (THP)
Poland: Beginning of the battle in the Vistula bend near Kutno, the last major engagement of the Polish campaign.
Western Front: The French army now occupies a 15-mile-wide front some five miles inside German territory. Although his forces have met no real opposition to its advance, General Maurice Gamelin halts his army and issues orders to prepare for a rapid retreat at the first sign of strong German opposition. General Gamelin brazenly lies to the beleaguered Poles when they protest the lack of French action; telling them that half of his active divisions are engaged in combat and meeting vigorous German resistance. "I have thus gone beyond my promise to take the offensive with the bulk of my forces by the fifteenth day after mobilization. It has been impossible for me to do more." Only 9 of France's 85 divisions on the frontier are employed in the 'offensive.'
1940 US Ambassador Grew in Japan to Secretary of State Hull:
Whatever the intentions of the present Japanese Government may be there cannot be any doubt that the military and other elements in Japan see in the present world situation a "golden opportunity" to carry their dreams of expansion into effect; the German victories, like strong wine, have gone to their heads; they have believed implicitly until recently in Great Britain's defeat; they have argued that the war will probably be ended in a quick German victory and that Japan's position in Greater East Asia should be consolidated while Germany is still agreeable and before Japan might be robbed of her far-flung control in the Far East by the eventual hypothetical strengthening of the German naval power; although carefully watching the attitude of the United States they have discounted effective opposition on our part. [For the full text, Click here.]

1941 Various:
Barbarossa: German forces in the Kremenchug bridgehead across the Dnepr in the Ukraine advance north to aid in the encirclement of Kiev. The first snow slows the Wehrmarcht's advance. (Clark II)

Holocaust: General Wilhelm Keitel tells his officers: "The struggle against Bolshevism demands ruthless and energetic measures above all against the Jews."
Holocaust: In the Ukrainian village of Zwiahel (Novograd Volynsky), SS 2nd Lieutenant Max Taubner and members of his work platoon begin conducting a series of unauthorized massacres of Jews. Täubner will later be tried and convicted by the SS and Police Supreme Court on May 24, 1943. (THP)
1942 Various:
War at Sea: Sinking of the Laconia:
On this day in 1942, a German U-boat sinks a British troop ship, the Laconia, killing more than 1,400 men. The commander of the German sub, Capt. Werner Hartenstein, realizing that Italians POWs were among the passengers, strove to aid in their rescue.
The Laconia, a former Cunard White Star ship put to use to transport troops, including prisoners of war, was in the South Atlantic bound for England when it encountered U-156, a German sub. The sub attacked, sinking the troop ship and imperiling the lives of more than 2,200 passengers. But as Hartenstein, the sub commander, was to learn from survivors he began taking onboard, among those passengers were 1,500 Italians POWs. Realizing that he had just endangered the lives of so many of his fellow Axis members, he put out a call to an Italian submarine and two other German U-boats in the area to help rescue the survivors.
In the meantime, one French and two British warships sped to the scene to aid in the rescue. The German subs immediately informed the Allied ships that they had surfaced for humanitarian reasons. The Allies assumed it was a trap. Suddenly, an American B-24 bomber, the Liberator, flying from its South Atlantic base on Ascension Island, saw the German sub and bombed it-despite the fact that Hartenstein had draped a Red Cross flag prominently on the hull of the surfaced sub. The U-156, damaged by the air attack, immediately submerged. Admiral Karl Donitz, supreme commander of the German U-boat forces, had been monitoring the rescue efforts. He ordered that "all attempts to rescue the crews of sunken ships...cease forthwith." Consequently, more than 1,400 of the Laconia's passengers, which included Polish guards and British crewmen, drowned. (History.com)
Holocaust: SS Obersturmbannfuehrer Liebehenschel to commanders of concentration camps:
According to a communication of the Chief of the Security Police and the SD, and conforming to a report of the Chief of the Security Police and the SD in Prague, urns of deceased Czechs and Jews were sent for burial to the home cemeteries within the Protectorate. In view of different events (demonstrations, erecting of posters inimical to the Reich on urns of deceased inmates in the halls of cemeteries of the home communities, pilgrimages to the graves of deceased inmates, etc., within the Protectorates, the delivery of urns with the ash remnants of deceased nationals of the Protectorate and of Jews is henceforth prohibited. The urns shall be preserved within the concentration camps. In case of doubt about the preservation of the urns oral instructions shall be available at this agency.
The Polish Army is formed in Iraq from Command in the Middle East and Polish Military Forces in the USSR are evacuated to Iran. Note: In 1943 the army is transferred to Palestine in preparation for the Italian Campaign, and the Polish 2nd Corps will leave from here for Europe.
1943 World War II: Mussolini is rescued by SS commandos at Gran Sasso, Italy, and after visiting with Hitler will become head of a puppet government in northern Italy. SS major Otto Skorzeny, the leader of the mission, becomes an instant German celebrity.
[See: How Did the Pact of Steel Effect Germany and Italy?]
Mussolini was first transferred to the tiny island Ponza, off Naples. Then he was moved to the tiny island La Maddalena, near Sardinia, where one of Skorzeny's Italian speaking commandos reported that he saw Mussolini from a distance in an isolated villa. Skorzeny then flew in a bomber to take aerial photos of the location. The bomber was shot down by allied fighters, but Skorzeny and the bomber's crew were rescued by an Italian destroyer. Mussolini's new location was picked by Herbert Kappler, the police attache in the German embassy in Rome, who intercepted a seemingly unimportant Italian police radio transmission referring to security preparations around Gran Sasso, the highest mountain in the Italian Apennines. Kappler immediately guessed that Mussolini is held in the ski hotel at the top of Gran Sasso, [which] was only accessible by cable car from the valley below. Further intelligence hints convinced the Germans that Mussolini might be on Gran Sasso. The Germans had to really hurry now.
1944 Various:

Churchill to General Ismay:
The British share in this war may take the form either of direct participation in particular United States enterprises in the Far East or of British diversionary enterprises on a major scale calculated to wear down the enemy forces by land and air, and also to regain British possessions conquered by the Japanese. Of the two, I favor the latter . . . . our policy should be to give navel assistance on the largest scale to the main American operation, but to keep our own thrust to Rangoon as a preliminary operation, or one of the preliminary operations, to a major attack of Singapore. Here is the supreme British objective in the whole of the Indian and Far Eastern theaters. It is the only prize that will restore British prestige in this region, and in pursuing it we render the maximum aid to the United States operations by engaging the largest numbers of the enemy in the most intense degree possible and at the earliest moment.
From a report prepared by the chief hygienist in the Office of the Reich Surgeon of the SS and Police:
On 11 September 1944, in the presence of SS Sturmbannfuehrer Dr. Ding, Dr. Widmann, and the undersigned, experiments with aconite nitrate bullets were carried out on five persons who had been sentenced to death. The caliber of the bullets used was 7.65 millimeters, and they were filled with poison in crystal form. Each subject of the experiment received one shot in the upper part of the left thigh, while in a horizontal position. In the case of two persons, the bullets passed clean through the upper part of the thigh. Even later no effect from the poison could be seen. These two subjects were therefore rejected . . . . The symptoms shown by the three condemned persons were surprisingly the same. At first, nothing special was noticeable. After 20 to 25 minutes, a disturbance of the motor nerves and a light flow of saliva began, but both stopped again. After 40 to 44 minutes, a strong flow of saliva appeared. The poisoned persons swallowed frequently; later the flow of saliva is so strong that it can no longer be controlled by swallowing. Foamy saliva flows from the mouth. Then a sensation of choking and vomiting starts. At the same time there was pronounced nausea. One of the poisoned persons tried in vain to vomit. In order to succeed he put four fingers of his hand, up to the main joint, right into his mouth. In spite of this, no vomiting occurred. His face became quite red. The faces of the other two subjects were already pale at an early stage. Other symptoms were the same. Later on the disturbances of the motor nerves increased so much that the persons threw themselves up and down, rolled their eyes, and made aimless movements with their hands and arms. At last the disturbance subsided, the pupils were enlarged to the maximum, the condemned lay still. Rectal cramps and loss of urine was observed in one of them. Death occurred 121, 123, and 129 minutes after they were shot.
US Army troops enter Germany near Trier.
Greece: German troops evacuate Rhodes and other Greek islands in the eastern Mediterranean.
Start of a German-Hungarian counter-offensive toward Arad and Temesvar in Hungary.
1945 War with Japan: The Japanese forces in Southeast Asia surrender to Admiral Mountbatten in Singapore. French troops land in Indochina.

1946 Nuremberg Tribunal: The justices meet to discuss verdicts in the Major War Criminals Trial. (See: 30 September 1946)
1953 Khrushchev elected Soviet leader:Six months after the death of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, Nikita Khrushchev succeeds him with his election as first secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. [For further details, Click here]

1959: Luna 2, a Russian satellite that has been sterilized to avoid contaminating the Moon with terrestrial bacteria, is launched.
[See: Wunderwaffen: Hitler's Deception and the History of Rocketry.]1974 Ethiopia: Emperor Haile Selassie is deposed by Ethiopia's military:

Haile Selassie I was Ethiopia's 225th and last emperor, serving from 1930 until his overthrow by the Marxist dictator Mengistu Haile Mariam in 1974. The longtime ruler traced his line back to Menelik I, who was credited with being the child of King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba.
For a country trying to gain its foothold in the young century and curry favor with the West, the progressive Tafari came to symbolize the hopes and dreams of Ethiopia's younger population. In 1923 he led Ethiopia into the League of Nations. The following year, he traveled to Europe, becoming the first Ethiopian ruler to go abroad.
His power only grew. In 1928 he appointed himself king, and two years later, after the death of Zauditu, he was made emperor and assumed the name Haile Selassie ("Might of the Trinity").
Over the next four decades, Haile Selassie presided over a country and government that was an expression of his personal authority. His reforms greatly strengthened schools and the police, and he instituted a new constitution and centralized his own power.
In 1936 he was forced into exile after Italy invaded Ethiopia. Haile Selassie became the face of the resistance as he went before the League of Nations in Geneva for assistance, and eventually secured the help of the British in reclaiming his country and reinstituting his powers as emperor in 1941.
Haile Selassie again moved to try to modernize his country. In the face of a wave of anti-colonialism sweeping across Africa, he granted a new constitution in 1955, one that outlined equal rights for his citizens under the law, but conversely did nothing to diminish Haile Selassie's own powers.
By the early 1970s famine, ever-worsening unemployment and increasing frustration with the government's inability to respond to the country's problems began to undermine Haile Selassie's rule.
In February 1974 mutinies broke out in the army over low pay, while a secessionist guerrilla war in Eritrea furthered his problems. Haile Selassie was eventually ousted from power in a coup and kept under house arrest in his palace until his death in 1975.
Reports initially circulated claiming that he had died of natural causes, but later evidence revealed that he had probably been strangled to death on the orders of the new government.
In 1992 Haile Selassie's remains were discovered, buried under a toilet in the Imperial Palace. In November 2000 the late emperor received a proper burial when his body was laid to rest in Addis Ababa's Trinity Cathedral. [For further information, click here.]
1990 Occupation rights in Germany relinquished:
Representatives from the United States, Great Britain, France, and the Soviet Union sign an agreement giving up all occupation rights in Germany. The largely symbolic action cleared the way for East and West Germany to reunite.
In 1945, the Allied Powers—America, England, France, and the Soviet Union—agreed that defeated Nazi Germany would be divided into four zones of occupation, one for each nation. Berlin would be likewise divided. The separation was intended to be temporary, but Cold War animosities quickly developed after World War II and the division between the Russian zone and those controlled by the other three nations became permanent. In the late 1940s, the American, French, and English zones were consolidated into West Germany and the Soviet zone became East Germany. The division came to symbolize the Cold War, and the divided Germany was the scene of many Cold War dramas, like the Berlin Airlift. In 1961, East German authorities began construction of the Berlin Wall, physically dividing East and West Berlin.
By 1989, however, the communist grip on East Germany was rapidly slipping away. The Soviet Union, facing its own severe economic and political problems, could do little to prop up the East German communist regime. In November 1989, the East German government announced that the Berlin Wall would be torn down. The next year, representatives from East and West Germany began negotiations to finally reunite their country. Among the many obstacles to overcome was the historical legacy of occupation by the Allied forces. Although the four Allies had long since removed their occupation forces and given up most of their occupation rights, some treaty rights still technically remained—for instance, the four countries still had the right to "oversee" Berlin. On September 12, 1990, representatives from the four nations met in Moscow and formally gave up all remaining occupation rights in Germany. Soviet Foreign Minister Eduard Shevardnadze declared, "We are going through emotional and historic events . . . We have drawn a line under World War II and we have started keeping the time of a new age." In October 1990, East and West Germany formally reunited under a democratic government. (History.com)
Edited by Levi Bookin (Copy editor)
levi.bookin@gmail.com



Click to join 3rdReichStudies



Disclaimer: This site includes diverse and controversial materials—such as excerpts from the writings of racists and anti-Semites—so that its readers can learn the nature and extent of hate and anti-Semitic discourse. It is our sincere belief that only the informed citizen can prevail over the ignorance of Racialist "thought." Far from approving these writings, this site condemns racism in all of its forms and manifestations.
Fair Use Notice: This site may contain copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of historical, political, human rights, economic, democracy, scientific, environmental, and social justice issues, etc. We believe this constitutes a "fair use" of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes. If you wish to use copyrighted material from this site for purposes of your own that go beyond 'fair use', you must obtain permission from the copyright owner.
Please Note: The list-owner and moderators of 3rdReichStudies are not responsible for, and do not necessarily approve of, the random ads placed on our pages by our web server. They are, unfortunately, the price one pays for a 'free' website.