Tutorial Index Page
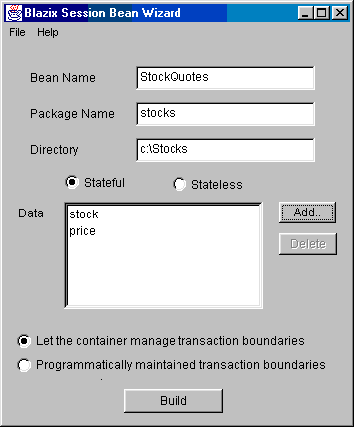
Creating a Session BeanSession beans have a framework similar to entity beans, but a little simpler. They have a remote interface and a home interface, but no primary key. They also do not need to be backed by a database or other form of permanent storage.Again, we will be using Blizzard to generate our basic framework. Our session bean will be a stock-price quoting agent. It will live on a machine where current stock prices are available. (We will just put a file with stock prices in it, in some fixed place like C:\StockPrices.txt!) The clients of the session bean will be able to specify a stock and obtain its current price. To create the session bean, run the Blazix EJB wizard Blizzard, and select "Create a Session bean". Fill in the bean name, package name and diretory name. Select "stateful" and "let the container manage transacton boundaries". Add data items "stock" (String) and "price" (float). We do not want a "setter" for "price", but make sure to provide a setter for "stock". Sample input is shown below.
Build the framework examine the files created by the wizard. Look in the remote interface, the home interface and the bean class. Everything is similar to the entity beans, but there is no primary key and therefore no findByPrimary key. Now we need to modify the framework so that the stock prices are read
from a file on the system. Create a file, e.g. "C:\StockPrices.txt"
and place some lines in it of the form
In the bean implementation file StockQuotesBean.java, add an import for java.io.* and delete the member variable "price". Also remove the "price" argument to the "ejbCreate" method and remove the statement where the "price" member variable is getting set. Change the implementation of "getPrice()" as follows. public float getPrice() throws java.rmi.RemoteException,
Notice that we have changed the function signature. Therefore go into the remote interface StockQuotes.java and add java.io.IOException to the exceptions-list of "getPrice()". Similarly, change the create signature in StockQuotesHome.java and remove "price". As before, create the bean by running the commands in the .cmd file. Exercise: Build another entity bean called "BankAccount".
This bean maintains an account for various users and lets them add and
substract amounts to it (perhaps the clients are tellers or ATMs!)
For now, keep a list of account names and their current balances in an
"accounts" text file. (Later, we will use JDBC for this purpose.)
The bean needs two data members, "name" and "balance".
There should be no setter for "balance". Add a "credit"
and a "debit" methods to the remote interface. Implement
getBalance,
credit
and debit by reading the file, and modifying it. To keep
things simple, "credit" and "debit" can just read the
lines of the file and write them to a temporary file. If the line
matches the current "name", they should write the new balance
instead of what was in the file. When done, delete the existing accounts
file and rename the temporary file to be the new accounts file.
|
||
|