
May 2 1670 1969

1519 Death: Leonardo da Vinci, near Amboise (Cloux), France, at 67. An Italian painter, sculptor, architect, and engineer, his genius epitomizes the Renaissance humanist ideal. "It may seem unusual to include Leonardo da Vinci in a list of paleontologists and evolutionary biologists. Leonardo was and is best known as an artist, the creator of such masterpieces as the Mona Lisa, Madonna of the Rocks, and The Last Supper. Yet Leonardo was far more than a great artist: he had one of the best scientific minds of his time. He made painstaking observations and carried out research in fields ranging from architecture and civil engineering to astronomy to anatomy and zoology to geography, geology and paleontology. In the words of his biographer Giorgio Vasari: The most heavenly gifts seem to be showered on certain human beings. Sometimes supernaturally, marvelously, they all congregate in one individual. . . . This was seen and acknowledged by all men in the case of Leonardo da Vinci, who had. . . an indescribable grace in every effortless act and deed. His talent was so rare that he mastered any subject to which he turned his attention. . . . He might have been a scientist if he had not been so versatile..."
1536 Queen Anne Boleyn, second wife of England's King Henry VIII, is sent to the Tower of London.
1611 The King James Version of the Bible is first published.
1668 War of Devolution: The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle, ends the conflict. "The War of Devolution (May 24, 1667 – May 2, 1668) was a war between Louis XIV's France and Habsburg Spain fought in the Spanish Netherlands. It was resolved in the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. The war was the first of Louis' wars of territorial aggrandizement. The prize: the rich market cities of the Catholic Low Countries and their long-established textile trade, which competed with French interests; the ports that offered advantageous positions opening on the English Channel and the North Sea; and opportunity to control river traffic at the mouth of the Rhine. Louis' claims upon the Spanish Netherlands were tenuous. His wife, Marie Thérêse, the daughter of Philip IV of Spain, had renounced her rights of a Spanish inheritance in return for a large dowry at the time of her marriage. The dowry had yet to be paid, however. When Philip finally died in 1665, Louis' lawyers justified Louis' possible claims by arguing that, while Spanish laws of succession meant the throne of Philip IV would pass to his son Carlos II, ancient laws of Brabant ruled that the Spanish Netherlands could "devolve" to Philip's daughter from his first marriage, Louis' wife. The French pressed the claim in 1667; the Spanish contested it. Louis began preparing for war..."

1729 Birth: Ekaterina Alekseevna, better known as Catharine the Great, empress of Russia 1762-96.
1776 US Revolutionary War: France and Spain collude to donate arms to American rebels.
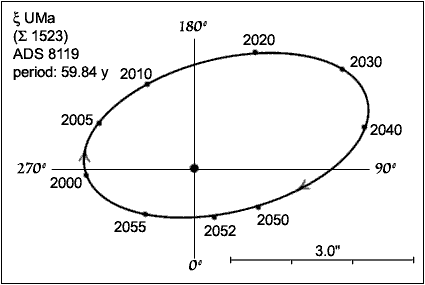
1780 Astronomer William Herschel discovers the first binary star, Xi Ursae Majoris.
1808 An uprising against French occupation begins in Madrid.

1813 Napoleonic Wars: During the Leipzig campaign, the French win the Battle of Lutzen.
1837 Birth: Henry Martyn Robert, US Army General, author; Robert's Rules of Order. "...Henry did not set out to be the leading authority in parliamentary procedure. He simply envisioned a need for a set of rules that were consistently followed everywhere. Therefore, when people moved to a new community, they would be able to use the same set of rules used in the previous community. He wrote a pamphlet which he shared with his friends. The response was encouraging. He then proceeded to write a book of his rules. He had trouble getting a publisher to print them. There were 4,000 copies of the first book printed with the idea that they would last a couple of years and then he would have enough comments for a revision. Instead, the copies sold out in a few months. That was the beginning of what is today the most recognized authority on parliamentary procedure. Much of the incredible logic of Robert’s Rules is explainable by his profession. He was a general in the US Army. He was an engineer. Now you understand his attention to detail and his ability to logically think through a problem. You also understand his desire for order at meetings. Not only was Robert the hero to those who attend lots of meetings, he was also a hero to the city of Galveston, Texas. He led his fellow engineers to design and construct the Galveston Seawall which safeguarded Galveston from the danger of damage from tropical storms..."

1853 Franconi's Hippodrome opens at Broadway and 23rd Street in New York City. The 4,000-seat facility's grand opening this day features a chariot-and-ostrich race.

1860 Birth: Theodor Herzl. "Viennese journalist and founder of modern political Zionism. Born in Budapest, Hungary, on May 2, 1860, Herzl was educated in the spirit of the German-Jewish "Enlightenment." The family moved to Vienna in 1878 after the death of his sister. He received a doctorate in law in 1884 and worked for a short while in courts in Vienna and Salzburg. Within a year, he left law and devoted himself to writing, for which he had demonstrated ability from an early age. In 1891 he became Paris correspondent for the New Free Press (Vienna), the influential liberal newspaper of the time. Herzl was in Paris to witness the rise of anti-Semitism which resulted from the court martial of Alfred Dreyfus, a Jewish army officer, who was divested of his rank in a humiliating public ceremony in January 1895, as a mob shouted "Death to the Jews." After considering a number of possibilities, Herzl became convinced that the only solution to the Jewish problem was the mass exodus of Jews from their places of residence. Originally he wrote that it didn't matter where Jews went. He eventually realized that a national home in Palestine was the answer..."
1863 US Civil War: The Battle of Chancellorsville, Virginia begins. Confederate General Thomas 'Stonewall' Jackson, accidentally wounded by one of his own men, will die eight days later.
1885 The Congo Free State is established by King Leopold II of Belgium. Considered the king's personal territory, it occupies most of the Congo River basin. In 1908 the Congo Free State will abolished and become the Belgian Congo, a colony controlled by the Belgian parliament. In 1966, the country will be named Zaire, and renamed the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1997.
1886 Birth: Gottfried Benn, Germany's foremost expressionist poet and an early, if temporary, supporter of National Socialism. Taking up where Goethe, Nietzsce, and Spengler left off, Benn despised the mechanized world and railed against rationalism and the political doctrines derived from it. By 1937, however, he had become disillusioned with Nazism and was driven out of the Reich Writers Association. Serving in the German army as a medical officer from 1939 to 1945, his postwar writings revealed the extent of his disillusionment with Nazism and his own vitalists irrationalism; the philosophy that initially was the motivation behind his regrettable flirtation with the Nazis.
1887 Hannibal W. Goodwin of Newark, New Jersey applies for a patent for celluloid photographic film.

1890 The Oklahoma Territory is organized.
1892 Birth: Manfred Freiherr von Richthofen, AKA The Red Baron, German WW1 ace.
1903 Birth: Dr Benjamin Spock, doctor, author; Common Sense Book of Baby Care. The first United States celebrity to speak out against the Vietnam War, he will support civil rights and do a commercial with Jacqueline Kennedy. Years before all that, he will be a trusted name in child care thanks to his books, which will tell parents to trust their instincts when raising a baby. Over the years he will update the book to incorporate nonsexist language and to emphasize the importance of a father in a child's life. He will be named as one of the 100 most important people in the 20th century by Life magazine.
1918 Weimar: Walter Riehl is elected chairman of the Austrian DAP (German Workers Party) and moves to Vienna.
1926 General Pilsudski believing that the unstable Polish parliamentary system is endangering Poland, seizes power and forms an authoritarian government. He works for good relations with both Germany and Russia, but an alliance with neither.
1931 Volkishness: Otto Rahn visits the castle of Montsegur in France, spending three months carefully exploring the local caves and grottos in search of the Holy Grail.
1933 The modern legend of the Loch Ness monster surfaces when a sighting makes the local news. There had been accounts of an aquatic beast living in Scotland's Loch Ness dating back 1,500 years.
1933 On Hitler's orders, all independent and Socialist trade unions in Germany are closed down and dissolved. The remains are united into the German Labor Front (DAF). (Lewy, Edelheit)
1933 Church and Reich: May 2-3 The central board of the Association of Catholic Young men decides that "the fact of belonging to the Jungmännerverein in principle does not rule out membership in the NSDAP, including its various formations (SA, SS etc.)." Soon afterward, the Nazi party forbids simultaneous membership in Catholic and National Socialist organizations. (Roth, Katholische Jugend)
1933 Germany outlaws the German Communist Party (KPD).
1935 Holocaust: Prussia's Administrative Court rules that the Gestapo is no longer subject to judicial control.
1935 May 2-6 France and the Soviet Union sign the Pact of Mutual Assistance in case of unprovoked aggression. Hitler says it is obviously directed at Germany.
1935 Birth: Faisal II, King of Iraq.
1936 Abyssinian Emperor Haile Selassie and his family flee Addis Ababa, three days before its capture by the Italians. Addis Ababa is looted and set afire by mobs.
1938 The Gestapo orders the Jewish community offices in Vienna reopened.

1941 WW2: Following a coup d'etat in Iraq, a pro-Nazi Government is formed. British airport in Habbania is attacked by Iraq troops.

1941 The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) agrees to let regular scheduling of TV broadcasts by commercial TV stations begin on 1 July 1941; the start of what will become network television in the US.

1942 WW2: HMS Edinburgh is sunk in the Barents Sea off Norway. Its cargo of gold bars will lay in 830ft of water until salvaged in 1981.

1945 WW2: The Soviet Union announces that Berlin has surrendered to the 1st White Russian and 1st Ukrainian armies; hostilities in Italy cease as Nazi troops surrender and also in parts of Austria. Hamburg opens negotiations for the surrender of the city.
1945 WW2: A mysterious SS convoy leaves the Berghof (Hitler's Eagle's Nest). Later that night, members of this SS detachment bury several crates and metal boxes at the foot of the Schleigeiss glacier. (Spear)
1945 WW2: British Second Army takes Lübeck and Wismar on the Baltic Coast. Canadian forces take Oldenburg.

1945 Nuremberg War Crimes Trials: US President Truman appoints Robert Jackson as chief US counsel for the prosecution of Nazi war criminals.

1951 The Council of Europe admits Germany as a full member.
1951 The Shah of Iran signs decrees approving the nationalization of its oil industry.
1952 The world's first ever scheduled jet airliner passenger service begins with a BOAC De Havilland Comet flight from London to Johannesburg carrying 36 passengers.
1953 In Jordan, King Hussein formally acceded to the throne after his father, King Talal, is deposed. In Iraq, King Feisal II assumes power.

1956 A US laboratory detects high-temperature microwave radiation from Venus.
1957 Death: Senator Joseph McCarthy, Republican senator, demagogue, at Bethesda Naval Hospital in Maryland, at 47.
1965 The first communications satellite for relaying television pictures goes into operation as Britain's Early Bird begins transmitting TV pictures to 300 million viewers in 24 countries.
1967 The Bertrand Russell International War Crimes Tribunal begins in Stockholm, later to find the United States guilty of aggression in Vietnam.
1972 Death: J. Edgar Hoover, after 48 years as head of the FBI, in Washington at the age of 77.
1982 Falklands War: The British submarine HMS Conqueror sinks the Argentine cruiser General Belgrano, with the loss of more than 350 lives.
1985 This is the day of reckoning for E.F. Hutton & Co., as the New York-based brokerage giant tenders a guilty plea to charges that it had engineered a massive checkwriting swindle. Standing before a court in Scranton, Pennsylvania, E.F. Hutton's lawyers admit that the firm had managed to soak hefty sums of money from its various bank accounts without paying a cent of interest. According to Attorney General Edward Meese, the firm wrote somewhere in the neighborhood of $4 billion in checks between the summer of 1980 and February 1982. In return for this complex, and lucrative, scheme, E.F. Hutton consents to pay roughly $10 million, which covered fines, as well as restitution to the victimized banks. However, none of the roughly twenty-four employees involved in the swindle faced criminal charges; Meese and his team grant some immunity and opt not to prosecute the rest on the grounds that they had not 'personally benefited' from their 'corporate scheme.'
1985 The last General Motors X-Car rolls off the assembly line in Detroit, Michigan. The cars were a dismal failure, despite being a hit in the beginning. The X-Cars were subject to massive recalls which cost GM many millions of dollars.
1989 Martial law is imposed in China as the government takes a firmer stand against pro-democracy demonstrators in Tiananmen Square. 60 Chinese students ride bicycles into Beijing to present demands for democratic reforms to Chinese leaders.
1990 The government of South Africa and the African National Congress opens their first formal talks aimed at paving the way for more substantive negotiations on dismantling apartheid.
1992 The Yugoslav Army seizes Bosnian President Alija Izetbegovic after fierce fighting in Sarajevo.
1993 Bosnian Serb leader Radovan Karadzic signs an internationally mediated peace plan to end the Bosnian conflict. All three warring factions in Bosnia-Herzegovina have now accepted the peace plan, but the fighting continues.
1993 The body of cult leader David Koresh is identified among the 72 taken from the charred rubble of the Branch Davidian compound. Officials say that Koresh had been shot in the head.
1994 President F.W. de Klerk concedes victory to Nelson Mandela in the country's historic first all-race elections. He will be inaugurated as the country's first black president eight days later.
1994 A Wayne County, Missouri jury, acquitted Dr. Jack Kevorkian of violating a state law forbidding assisted suicides.
1995 President Clinton agrees to allow some 20,000 Cubans into the United States after months of detention at Guantanamo Bay, but says that any more Cubans who flee their country will be repatriated.
1995 Serb missiles explode in the heart of Zagreb, killing six people.
1996 President Clinton vetoes a cap on punitive damage awards.
1997 The Labour Party led by Tony Blair wins a landslide victory in the British general election, ending 18 years of Conservative rule. John Major announces that he is stepping down as leader of Britain's Conservative Party.
1997 The White House and congressional negotiators reach an agreement intended to balance the federal budget by 2002.
1999 A meeting between the Reverend Jesse Jackson and Yugoslav President Slobodan Milosevic leads to the release of three US soldiers captured a month earlier by Serbian troops.
2001

2002

2002 The US Congress overwhelmingly approves a resolution supporting Israel's latest military operations against the Palestinians. Also, Israeli forces pull out of the West Bank city of Ramallah allowing Yassar Arafat to leave his compound.
2003

2004

2005

2005

2005

2005

2005

2005

Visit:




 Visit:
Visit:

Click Here to email the History: One Day At a Time webmaster.