 |
No. | Province | Area (sq. km.) | Pop. as of 1997 | |
| 1 | Kanchanaburi | 19,483.15 | 766,352 | ||
| 2 | Phetchaburi | 6,225.14 | 453,391 | ||
| 3 | Prachuab Khiri Kan | 6,367.62 | 468,880 | ||
| 4 | Ratchaburi | 5,196.46 | 813,293 | ||
| 5 | Tak | 16.406.65 | 471,596 |
 |
No. | Province | Area (sq. km.) | Pop. as of 1997 | |
| 1 | Kanchanaburi | 19,483.15 | 766,352 | ||
| 2 | Phetchaburi | 6,225.14 | 453,391 | ||
| 3 | Prachuab Khiri Kan | 6,367.62 | 468,880 | ||
| 4 | Ratchaburi | 5,196.46 | 813,293 | ||
| 5 | Tak | 16.406.65 | 471,596 |
Geography and Climate
Mountains and rivers: The West has 2 significant mountain ranges and
4 significant rivers:
|
of West Thailand 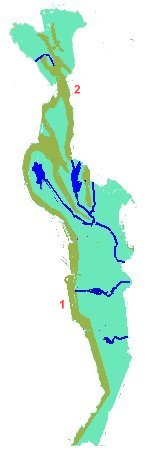 |
|
|
|||
| No. (Red) | Mountain Range | No. (Purple) | River | ||
| 1 | Tanaosri (Tenasserim) | 1 | Mae Klong | ||
| 2 | Thanon Thongchai | 2 | Kwae Noi | ||
| 3 | Kwae Yai | ||||
| 4 | Phetchaburi | ||||
Places of Interest
The East has many places of interest, for example:
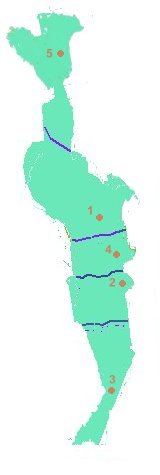
1. Hua Hin beach, Prachuab Khiri Kan Province and Cha Am beach, Phetchaburi
Province
Hua Hin beach is another important beach resort.
Like Pattaya (see East), Thais and foreigners alike
come here for their vacations. The neighbouring Cha Am beach is also popualr
among tourists.
2. Samroi Yot national park, Prachuab Khiri Kan Province
The first aquatic national park in Thailand, the
98 sq. km. park has various species of birds, complex limestone mountains
and low-lying plains along the coast.
3. Klai Kangwon Palace, Prachuab Khiri Kan Province
Built under order of King Pokklao in 1926 for Queen
Rampai Panni, the palace is set amongst a garden of various speices of
flowers with the coast on one side.
4. Bridge Over The River Kwae, Kanchanaburi Province and Death Railway,
Ratchaburi and Kanchanburi Provinces
The bridge was built during World War II by Japanese
POWs for their railway from Ban Pong in Ratchaburi Province to Tanbyusayak
in Burma. Most of the railway has since been removed, leaving the stretch
from Ban Pong to Namtok Station.
5. Jedi Samong Pass, Kanchanaburi Province
It has marked the border between the Burma, now
Myanmar, and Thailand for many centuries, and was also used to mark the
route of armies in the past.
6. Phumiphon Dam, Tak Province
Southeast Asia's biggest dam was built from 1953
to 1964 and provides water for farmers, protection against floods and electric
power.