SYMPTOMS :
Bladder stones or concrements cause pain during miction ; the cat's owner is alarmed by the presence of blood in the urine. In male cats urinary concrements can cause a total obstruction uf the urethra which then has to be rinsed by the veterinarian (photo 1); Without treatment there is a high risk of uremia and acute renal failure.

DIAGNOSIS
Large concrements can be seen on an X-ray. A urinalysis determines the urinary pH an the type of crystals. Bacteriological exam and antibiogram are necessary for a precise diagnosis.

THERAPY
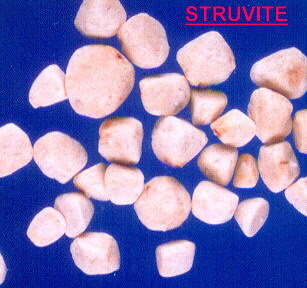
struvite :
Struvite crystals can be dissolved by decreasing the pH (pH<6) : methionine, ammoniumchloride or ascorbic acid are drugs that can be used to render the urinary pH more acid. Different brands of diet food that acidify the urine are sold by your veterinarian.
oxalate : Surgery is the only way to remove these concrements. Low protein, low sodium and low calcium diets can be useful as a preventive measure.
ammonium urate : No medical treatment, so surgery is required once again. Urinary pH should be stabilised around 7 in order to prevent crystallisation of ammonium urate.

If the urinalysis shows the presence of bacteria, antibiotic treatment (after antibiogram) should be performed for 3 to 6 weeks ( !)