2. Worked as a Research Associate on a research contract in
Department/University:
Department of Mechanical and Process
Engineering, University
of Sheffield
Mappin Street, Sheffield S13JD,

A View of Administrative
Building of
Period: August 1987 to Dec. 1989
Project
Title:
An
Investigation into the Stresses associated with Compressor
Blade/Disc Fixings
Project Supervisors
Scope of Project
This is a collaborative
research project between Rolls-Royce plc,

Typical Rolls Royce Engine:
The
experimental stress analysis technique of photoelasticity is one of the most
versatile methods available which enables both boundary and internal stresses
to be determined.
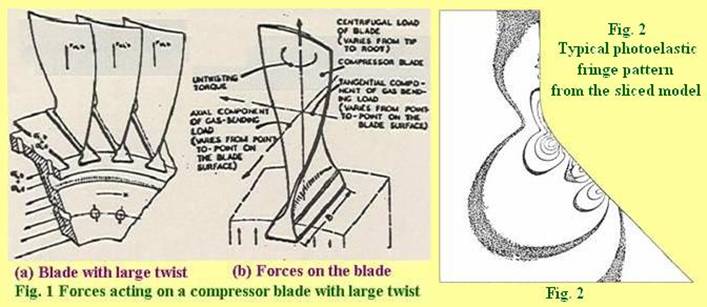
The ultimate aim of the
project is to investigate using detailed photoelastic analysis, the stress
distributions around the fillet and contact zones of the fir-tree root type of
blade fixing. Previous theoretical and photoelastic stress analyses of these
fixings indicate that a maximum stress occurs in the root fillet radius but
away from the contact zone. Failure evidence however shows that some cracks
initiate from sites within the contact zone. The major aim of the project is to
analyze the effect
of various
parameters such as tooth geometry, load distribution along the flanks, and the
frictional effects due to the relative motion between the teeth, on the
stresses found in the fillet regions and the contact zones.
Extensive
photoelastic investigations on simplified two-dimensional blade models with
different flank angles (0°, 30° and 45°) and contact conditions were conducted.
It was followed by a series of studies on the slices cut from a three
dimensional stress-frozen bladed-disk photoelastic model (slices were supplied by
Rolls Royce). A slice analyzer with high optical resolution was used in these
investigations.
Typical results of the investigations are presented below:


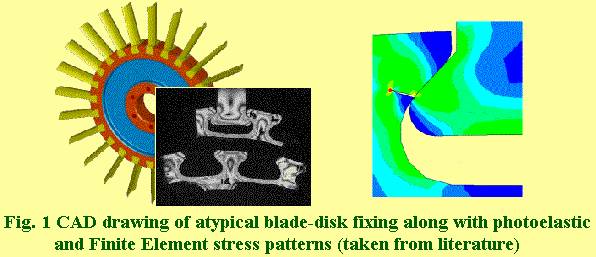
Analysis on three-dimensional stress frozen model (Slice Analysis):
1.
Kenny,
B., Patterson, E. A., Said, M., Aradhya, K. S. S., 'Contact stress distributions in a turbine
disc dovetail type joint - a comparison
of photoelastic and finite element results', Strain, 27(1): 21 - 24.
2. B. Kenney, E.A. Patterson and K. S. S. Aradhya, 'Photoelastic analysis of dovetail joints for turbine blades', Proc., Conference on Applied Stress Analysis held at the University of Nottingham, Nottingham, N67 2RD, ENGLAND, during August 30-31, 1990.
|
Appointment |
Research Interests |
Publications
|
Positions Held |
Academic
Experience
| Students |
Citations |
Courses |
|
My Alma mater |
My Teachers |
Foreign Assignments |
My Friends |
My Colleagues
| My Family |
|
Route Map to my Residence (RMV Clusters) |