|
 >>> >>>
|
| IMPACT
OF THE PANAMA CANAL TREATY ON THE U.S. MILITARY - continued
PANAMA CANAL
TREATY DESIGNATIONS FOR U.S. MILITARY INSTALLATIONS
The
following were the U.S. bases, installations, and facilities
covered by the Panama Canal Treaty of 1977 and associated
documents (Agreement in Implementation of Article IV of that
Treaty) which entered into force October 1, 1979. Some were
designated as Defense Sites while the others were designated
Military Areas of Coordination (for housing, training, special
facilities or General Military Areas of Coordination). Earlier
inactive bases, installations, and facilities that had either been
transferred to Panama under earlier agreements are not covered by
this treaty. Those bases or facilities are covered in a related
section, Description of U.S. Bases/Installations in Panama
(1910-1999).
Defense
Sites were those areas (and facilities within them) which Panama
permitted the U.S. Forces to use for the specific purposes of the
Panama Canal Treaty and as the two governments otherwise agreed.
The Defense Sites were for the exclusive use of the U.S. Forces
and were under their complete control for the life of the Panama
Canal Treaty.
Military
Areas of Coordination were those areas and facilities which Panama
permitted the U.S. Forces to use for the purposes of
communications and military training and for housing and support.
With the exception of Special Facilities, their security was the
combined responsibility of both countries; nevertheless, the
senior U.S. Forces commander had ultimate responsibility for
internal security of these forces.
|
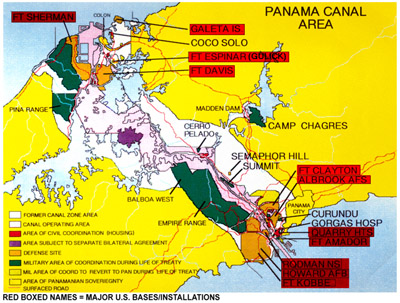
|
PANAMA
CANAL
AREA TREATY MAP --This map is based on the one among the Attachments to Annex A to the
Panama Canal Treaty of 1977). Popularly called "the
Treaty map," it denotes the major U.S. military
installations and facilities (brown for Defense Sites
and green for Military Areas of Coordination) and the
principal Panama Canal Commission facilities (red for
PCC housing areas and pink for Panama Canal Operating
Area, such as the Canal and its supporting facilities),
as defined by Treaty. One can appreciate what remained
under
United
States
control after October
1, 1979,
when the former Canal Zone
was abolished with the implementation of the Panama Canal
Treaty (with the white areas denoting former Canal
Zone
areas transferred to Panama
on
that date). [Source:
U.S.
Southern Command
Directorate of Treaty Implementation]
|
Defense
sites:
Pacific
Side of the isthmus:
 | Howard
Air Force Base
 | Fort
Kobbe (including Cocoli Housing Areas and Rodman Ammuntion
Storage Area)
 | U.S.
Naval Station, Rodman (including the Farfan Radio Receiver
Facility and the Arraijan Tank Farm)
 | Marine
Barracks
 | Fort
Clayton (including Corozal East and West)
 | Semaphore
Hill Long-Range Radar and Communications Link |
| | | | |
Atlantic
side of the isthmus:
 | Fort
William D. Davis
 | Fort
Sherman
 | Galeta
Island
 | U.S.
Navy Transisthmian Pipeline (across the isthmus) |
| | |
Military
areas of coordination (MAC):
General
Military Areas of Coordination (Pacific
side):
 | Quarry
Heights
 | U.S.
Naval Station Panama Canal, Fort Amador |
|
General
Military Areas of Coordination (Atlantic
side):
 | Fort
Gulick (later named by Panama Fuerte Espinar) |
Military
Areas of Coordination for Training (Pacific
side):
 | Empire
Range Training Complex
 | Fort
Clayton Training Area |
|
Military
Areas of Coordination for Training (Atlantic
side):
 | Pina
Range
 | Fort
Sherman West Training Area |
|
Military
Training Areas for Housing (Pacific side):
 | Fort
Amador (except for Buildings 1 through 9; 45 through 48; 51,
57, 64, and 93, and eight family housing units which were
transferred to Panama on October1, 1979)
 | Curundu
Heights (except for 20 family housing units transferred to
Panama on October 1, 1979)
 | Curundu
Flats
 | Herrick
Heights |
| | |
Military
Training Areas for Housing (Atlantic
side):
 | Coco
Solo South
 | France
Field |
|
Military
Areas of Coordination-Special Facilities: (following list does
not include every facility listed in paragraph (3)(a)(iv) of Annex
A, "Defense Sites, Military Areas of Coordination and Other
Installations," of Panama Canal Treaty: Agreement in
Implementation of Article IV)
Those
facilities below listed in red denote transfer on October 1, 1979,
to the Department of Defense from the former Canal Zone Government
(which was abolished with the entry into force of the Panama Canal
Treaty same date).
Those
facilities listed in green denote transfer to the Department of
Defense from the Panama Canal Company (predecessor of the Panama
Canal Commission) on October 1, 1979.
Pacific side (Special
Facilities):
 | Gorgas
Hospital Complex
 | Mortuary
 | Quarry
Heights Communications Facility (Tunnel)
 | Curundu
Antenna Farm
 | U.S.
Navy Communications Facility (at Fort Amador)
 | Summit
Naval Radio Station
 | Ancon
Hill Communications Facility
 | Balboa
High School, Curundu Junior High School, Balboa Elementary
School, Diablo Elementary School, Los Rios Elementary School,
Gamboa Elementary School, Cristobal Junior-Senior High School,
Panama Canal College
(The schools located on military bases -- at Fort Clayton,
Fort Kobbe, Howard Air Force Base, Fort Gulick and Fort Davis
-- were considered as part of the installations where they
were located.)
 | Health
Centers at Balboa and Gamboa
 | Ancon
Dental Clinic
 | Corozal
Mental Health Center
 | Corozal
Animal Care Station/Veterinary Hospital
 | Corozal
Cemetary
 | Balboa
Commissary
 | Following
facilities located in the Curundu PAD (former Panama Air
Depot) Area (Remainder of the PAD area transferred to Panama
on October 1, 1979): Defense Mapping Agency-InterAmerican
Geodetic Survey (DMA-IAGS), Medical Department Activity (MEDDAC)
warehouse, and Army and Air Force Exchange System (AAFES)
warehouses
 | Laundry
at Ancon
and Army Laundry at Curundu
 | Camp
Chagras Boy Scout Camp at Madden Dam
 | Surfside
Theater at Naos Island
 | Cerro
Pelado Ammunition Transfer Point |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Atlantic
side(Special Facilities):
 | Coco
Solo Hospital Complex
 | Cristobal
Junior-Senior High School, Coco Solo Elementary School,
Margarita Elementary School, Fort Gulick Elementary School,
and Canal Zone College (Panama Canal College)
 | Health
Centers at Margarita and Coco Solo
 | Ammunition
Supply Point (ASP) on Fort Gulick
 | Battery
Pratt Communications Facility (near Fort Sherman)
 | Mindi
Veterinary Clinic |
| | | | |
|
|
| This
page last updated: July
4, 2008 |
 |
| Site
developed, owned and maintained by |
| William
H. Ormsbee, Jr. 1999-2001 / 2005-2008 |
|
(Including
WHO's IN
RETROSPECT website
1999-2001) |
|
PANAMA
CANAL TREATY TRANSITION
Treaty Impact on Canal
Operations
Treaty Impact on Military
- Military Forces
Drawdown
- Military Property
Transfers to Panama
Treaty Transition
overview
Text
of the Panama Canal Treaty and the Neutrality Treaty
____________
MILITARY
PROPERTIES TRANSFERRED TO PANAMA (1979-1999)
Total of 95,293 acres (with 5,237
buildings and other facilities mostly on 12 major active military bases)
All together worth over $4 billion
dollars (conservative estimate)
Transferred to Panama at no cost as
stipulated by the Panama Canal Treaty
____________
MILITARY
BASES TRANSFERRED
1979
Part of the Army sector of Fort Amador
Albrook Army Airfield with airstrip at
Albrook
1984
Part of Fort Gulick (Army School of
Americas buildings, barracks, etc.)
1995
Fort Davis and remainder of Fort Gulick
1996
Fort Amador (Navy sector and remainder of
Army sector)
1997
Albrook Air Force Station
1998
Quarry Heights
1999
Marine Barracks
Rodman Naval Station
Fort Sherman
Galeta Island
Fort Kobbe
Fort Clayton
Howard Air Force Base
East and West Corozal
|