|
The
Word
The
term "fire wall" originally meant, and still means,
a fireproof wall intended to prevent the spread of fire
from one room or area of a building to another. The Internet
is a volatile and unsafe environment when viewed from a
computer-security perspective, therefore "firewall"
is an excellent metaphor for network security.
In
computer networking, the term firewall
is not merely descriptive of a general idea. It has come
to mean some very precise things.
Location,
Location, Location
The
most important aspect of a firewall is that it is at
the entry point of the networked system it protects.
In the case of Packet Filtering, it
is at the lowest level, or "layer" in the hierarchy
(stack) of network processes, called the Network Layer or the
Internet Layer. This means essentially that the firewall
is the first program or process that receives
and handles incoming network traffic, and it is the last
to handle outgoing traffic.
The
logic is simple: a firewall must be positioned to
control all incoming and outgoing traffic. If some
other program has that control, there is no firewall.
So
-- what do firewalls do?
Packet
Filtering
All
Internet traffic travels in the form of packets.
A packet is a quantity of data of limited size, kept small
for easy handling. When larger amounts of continuous data
must be sent, it is broken up into numbered packets for
transmission and reassembled at the receiving end. All your
file downloads, Web page retrievals, emails -- all these
Internet communications always occur in packets.
A
packet is a series of digital numbers basically, which conveys
these things:
- The
data, acknowledgment, request or command from the originating
system
- The
source IP address and port
- The
destination IP address and port
- Information
about the protocol (set of rules) by which the packet
is to be handled
- Error
checking information
- Usually,
some sort of information about the type and status of
the data being sent
- Often,
a few other things too - which don't matter for our purposes
here.
In
packet filtering, only the protocol and
the address information of each packet
is examined. Its contents and context (its relation to other
packets and to the intended application) are ignored. The
firewall pays no attention to applications on the host or
local network and it "knows" nothing about the
sources of incoming data.
Filtering
consists of examining incoming or outgoing packets and allowing
or disallowing their transmission or acceptance
on the basis of a set of configurable rules, called policies.
Packet
filtering policies may be based upon any of the following:
- Allowing
or disallowing packets on the
basis of the source IP address
- Allowing
or disallowing packets on the
basis of their destination port
- Allowing
or disallowing packets according to protocol.
This
is the original and most basic type of firewall.
Packet
filtering alone is very effective as far as it goes but
it is not foolproof security. It can potentially
block all traffic, which in a sense is
absolute security. But for any useful networking to occur,
it must of course allow some packets to pass. Its weaknesses
are:
- Address
information in a packet can potentially be falsified or
"spoofed" by the sender
- The
data or requests contained in allowed packets may ultimately
cause unwanted things to happen, as where a hacker may
exploit a known bug in a targeted Web server program to
make it do his bidding, or use an ill-gotten password
to gain control or access.
An
advantage of packet filtering is its relative simplicity
and ease of implementation.
Circuit
Relay
Also
called a "Circuit Level Gateway,"
this is a firewall approach that validates connections before
allowing data to be exchanged.
What
this means is that the firewall doesn't simply allow or
disallow packets but also determines whether the connection
between both ends is valid according to configurable rules,
then opens a session and permits traffic only from the allowed
source and possibly only for a limited period of time. Whether
a connection is valid may for examples be based upon:
- destination
IP address and/or port
- source
IP address and/or port
- time
of day
- protocol
- user
- password
Every
session of data exchange is validated and monitored and
all traffic is disallowed unless a session is open.
Circuit
Level Filtering takes control a step further than a Packet
Filter. Among the advantages of a circuit relay is that
it can make up for the shortcomings of the ultra-simple
and exploitable UDP protocol, wherein the source address
is never validated as a function of the protocol. IP spoofing
can be rendered much more difficult.
A
disadvantage is that Circuit Level Filtering operates at
the Transport Layer and may require
substantial modification of the programming which normally
provides transport functions (e.g. Winsock).
Application
Gateway
In
this approach, the firewall goes still further in its regulation
of traffic.
The
Application Level Gateway acts as a proxy
for applications, performing all data exchanges with the
remote system in their behalf. This can render a computer
behind the firewall all but invisible to the remote system.
It
can allow or disallow traffic according to very specific
rules, for instance permitting some commands to a server
but not others, limiting file access to certain types, varying
rules according to authenticated users and so forth. This
type of firewall may also perform very detailed logging
of traffic and monitoring of events on the host system,
and can often be instructed to sound alarms or notify an
operator under defined conditions.
Application-level
gateways are generally regarded as the most secure type
of firewall. They certainly have the most sophisticated
capabilities.
A
disadvantage is that setup may be very complex, requiring
detailed attention to the individual applications that use
the gateway.
An
application gateway is normally implemented on a separate
computer on the network whose primary function is to provide
proxy service.
As
you can see, all firewalls regardless of type have one very
important thing in common: they receive, inspect and make
decisions about all incoming data before
it reaches other parts of the system or network. That means
they handle packets and they are strategically
placed at the entry point to the system
or network the firewall is intended to protect. They usually
regulate outgoing data as well. The types
and capabilities of firewalls are defined essentially by:
- Where
they reside in the network hierarchy (stack);
- how
they analyze and how they regulate the flow of data (packets);
- and
additional security-related and utilitarian
functions they may perform. Some of those additional functions:
- data
may be encrypted/decrypted by the firewall for secure
communication with a distant network
- Scripting
may allow the operator to program-in any number of
specialized capabilities
- The
firewall may facilitate communications between otherwise
incompatible networks.
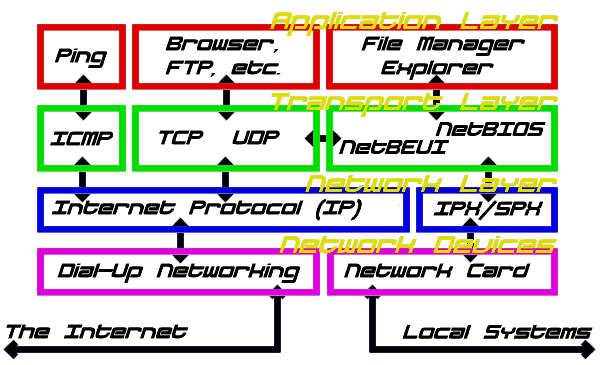
A
rough approximation of the "stack"
in a typical Win9x machine on a household LAN and with dial-up:
|

